 Jumpers—A General Explanation
Jumpers—A General ExplanationDell™ PowerEdge™ 1750 Systems Service Manual
 SCSI Backplane Board Connectors
SCSI Backplane Board Connectors
This section provides specific information about the jumpers on the system board. It also provides some basic information on jumpers and switches and describes the connectors and sockets on the various boards in the system.
Jumpers provide a convenient and reversible way of reconfiguring the circuitry on a printed circuit board. When reconfiguring the system, you may need to change jumper settings on the system board. You may also need to change jumper settings on expansion cards or drives.
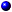
Jumpers are small blocks on a circuit board with two or more pins emerging from them. Plastic plugs containing a wire fit down over the pins. The wire connects the pins and creates a circuit. To change a jumper setting, pull the plug off its pin(s) and carefully fit it down onto the pin(s) indicated. Figure 5-1 shows an example of a jumper.

|
CAUTION: Make sure the system is turned off before you change a jumper setting. Otherwise, damage to the system or unpredictable results may occur. |
A jumper is referred to as open or unjumpered when the plug is pushed down over only one pin or if there is no plug at all. When the plug is pushed down over two pins, the jumper is referred to as jumpered. The jumper setting is often shown in text as two numbers, such as 1-2. The number 1 is printed on the circuit board so that you can identify each pin number based on the location of pin 1.
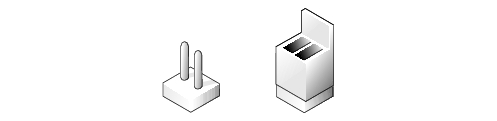
Figure 5-2 shows the location and default settings of the jumper blocks on the system board. See Table 5-1 for the designations, default settings, and functions of the system's jumpers.
Figure 5-2. System Board Jumpers

Table 5-1. System Board Jumper Settings
See Figure 5-3 and Table 5-2 for the descriptions and locations of the system board connectors.
Figure 5-3. System Board Connectors and Sockets
Table 5-2. System Board Connectors and Sockets
|
Connector or Socket |
Description |
|---|---|
NOTE: If you purchased a 400-MHz front-side bus system with a preinstalled Gigabit PCI network card, the integrated NIC connectors are nonfunctional. | |
Cooling fan power connectors (six on system board; one on control panel assembly) | |
Figure 5-4 shows the location of the connectors on the top of the SCSI backplane board.
Figure 5-4. Connectors on the SCSI Backplane Board
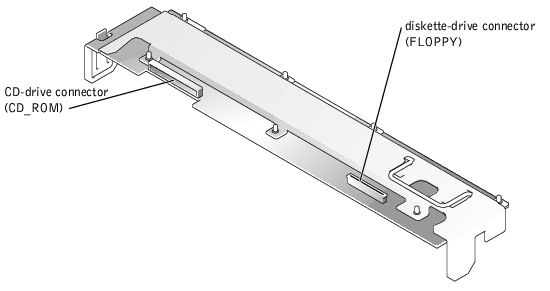
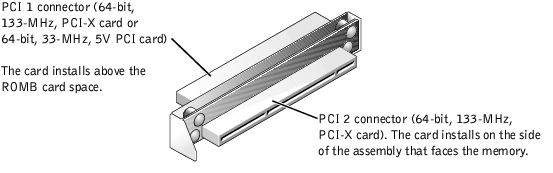
Figure 5-5 identifies the two PCI-X card connectors on the PCI riser board assembly.
Figure 5-5. Riser-Board Expansion-Card Connectors