COMMS # 59
 |
FECO:
|
COMMS
# 59 |
|
MODIFICATION NO:
|
N/A |
|
PRODUCT:
|
CISCO
1605 ROUTERS |
|
SUB-ASSEMBLY:
|
N/A |
|
ESTIMATED MAN HOURS:
|
N/A |
|
CLASS OF CHANGE:
|
INFORMATIONAL |
|
REASON FOR CHANGE:
|
INTRODUCTION
OF CISCO 1605R ROUTER |
|
RELATED FECO/AB
|
FECO
COMMS # 58 & 60 |
CISCO 1605R ROUTER
1 NOTE: Throughout
this FECO a SPACE in a string is shown by a — .
All other spaces are purely cosmetic
2 This is to
introduce the Cisco 1605R ISDN / Kilostream Router.
The Cisco
Routers can be used to replace the 3Com Office Connect 531’s.
The 1605 is shown below.
3 The 1605 is
modular. The rear diagram shows the slot for the WAN Module on the right, with the
thin slot
beneath it for the Software Flash Card. The Console connection and LAN connectors are
also shown.
The power input from the external PSU is shown bottom right, with the cord retaining clip.
4 For General
Information refer to FECO COMMS#58
5 SPECIFICATION
The
standard 1605 comes with two LAN interfaces, a 10BaseT and the other is a 10BaseT/AUI.
The 1605 R routers have a "run from RAM" architecture; the "R" suffix
designates run from
"RAM". The Cisco IOS software image is stored in Flash memory (in compressed
form), but is
loaded into RAM before being executed by the router.
The Run-from-RAM models offer the following benefits:
Greater Performance – The Cisco 1605 R models deliver greater performance for memory
intensive applications such as encryption and compression.
Easier Upgradability – The Cisco 1605 R routers permit software upgrades over any
interface
while
the router is running.
Lower Cost – Because the 1605 R models store the software in compressed form in Flash
memory, less flash memory is required to run advanced feature sets (such as Cisco 1600
series
IOS
IP Plus).
Cisco 1600 series routers offer small businesses and small branch offices a complete set
of
internetworking software features. Cisco IOS software differentiates the Cisco 1600 series
from
the
competition with:
Multiprotocol routing (IP, IPX, AppleTalk), IBM/SNA, and transparent bridging over ISDN,
asynchronous serial, and synchronous serial such as leased lines, Frame Relay, SMDS,
Switched 56, X.25, and X.25 over D.
Network Address Translation (NAT), which eliminates the need to re-address all hosts with
existing
private network addresses and hides internal addresses from public view.
Easy IP – a combination of NAT, Point-to-Point Protocol/Internet Control Protocol.
(PPP/IPCP) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server – which enables the
router
to
dynamically negotiate its own IP address and dynamically allocate local IP addresses to
the
remote LAN hosts, simplifies deployment, and minimizes Internet access costs.
End-to-End QoS features such as Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP), IP Multicast, WFQ,
and
AppleTalk Simple Multicast Routing Protocol (SMRP), which support multimedia applications
such
as desktop video conferencing, distance learning, and voice/data integration.
WAN optimisation features such as dial-on-demand routing (DDR), bandwidth-on-demand (BOD),
and
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)-on demand circuit, Snapshot routing, compression,
filtering,
and
spoofing to reduce WAN costs.
SIZE approx 11.5 x 2.5 x 9 inches 28.5 x 6 x 22 cm with external PSU.
6 OPTIONS
There
are six different WAN Interface modules and twelve different Software Features Packs.
Most
WAN Interface modules are compatible with other Cisco Models.
7 MEC IDENTITY
CISCO-1605R-ETH-ROUTER
Cisco 1605
CISCO-1PORT-ISDN-WAN-I/F
ISDN WAN Interface
Module
CISCO-1PORT-SERIAL-WAN-I/F Kilostream WAN Interface
Module
NOTE The two WAN Interface Modules are common to other Cisco Models like the
1700, 2600
and 3600 Series Models.
8 BASIC
INSTALLATION
8.1 WARNING
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN interface card ports regardless of whether
power
to the
router is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports.
When
detaching cables, detach the end away from the router first.
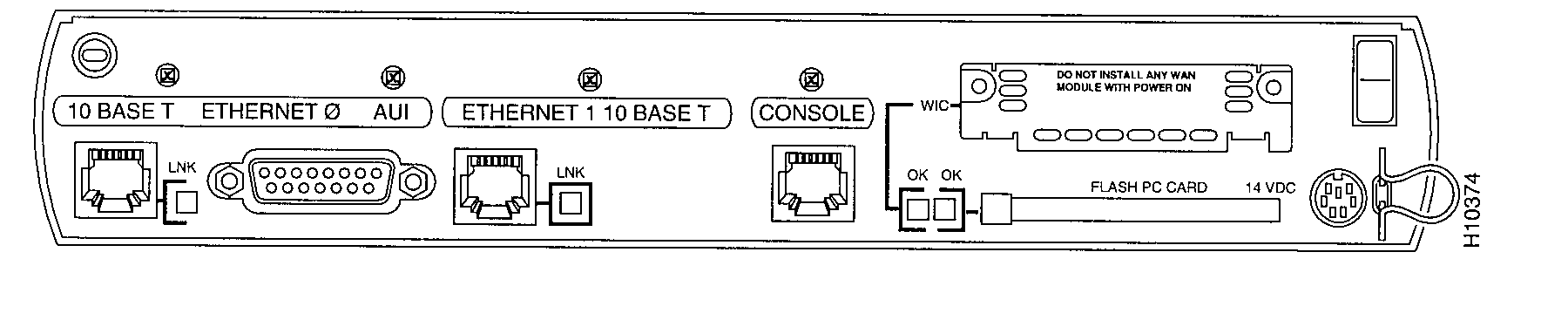
8.2 FLASH PC CARD
Insert the
Flash PC Card into the slot labelled FLASH PC CARD connector edge first, writing
uppermost.
When correctly seated it should just protrude.
8.3 LAN CONNECTION
Connect the
router to you local Ethernet network(s). The router can be connected to one or two
local networks.
It cannot be connected to three.
8.4 WAN CONNECTION
Install a WAN
interface card. The router cannot make any connections outside the local network
unless a WAN
interface card is installed and connected. Without a WAN interface card installed,
the router does
function correctly between two local networks. Look for a WAN interface card in the
slot on the
right-rear of the router, just above the slot labelled FLASH PC CARD. (There is no WAN
interface card
installed if there is a metal plate over the slot.) If the card is already installed,
connect
it to your WAN
line according to the instructions that came with the card. To install a card, follow the
instructions
below.
Confirm that
the power is OFF.
Remove the
thumbscrews that hold the slot cover in place, and then remove the slot cover.
Hold the card
by the edges and line it up with the guide on the card slot.
Insert the
card into the slot and push in until it is firmly seated in the connector and front panel
is flush
with the router
rear panel.
Tighten the
screws that are in the card.
Connect the
card port to the WAN line according to the instructions that came with the card.
8.5 POWER CONNECTION
Connect the
power supply. After you connect the power, you can confirm proper installation by
checking that
certain LEDs are on.
Connect the
power supply cord to the power socket on the rear panel, use the cord retaining clip to
hold/secure it.
Connect to
power supply to a power outlet and switch on.
Confirm that
the router has power by checking that the SYSTEM PWR LED on the front panel is on.
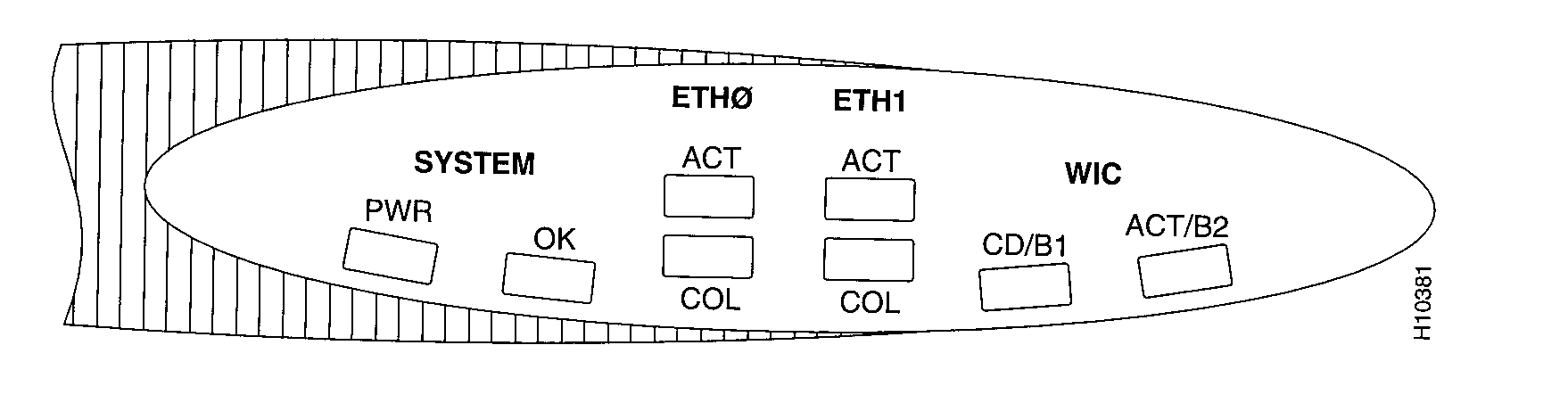
8.6 LED
Location
What to Look For
SYSTEM
Front
On
means that power is being supplied to the router.
PWR
System
OK Front
On
means that the router software is loaded and functional.
Blinking means that the software is being loaded into router
memory.
OK
Rear,
to the left of On means that the
Flash PC card is correctly installed. If
the
Flash PC card the LED is off, refer to the
hardware installation guide that
slot
came with the router for instructions on how to re-install the card.
LNK
Rear, one next to On means that the
router is connected to a local Ethernet
each 10BaseT
network through this port. If you connected the router to a
port
local network through the AUI port, then the LNK LED next
to the ETHERNET ∆ 10BASET should be off.
ETH∆ ACT
Front
Blinking means that there is network traffic on the local
Ethernet network that is connected to the ETHERNET ∆
10BASET port or the ETHERNET ∆ AUI port (only one of
these two ports should be connected).
ETH1 ACT
Front
Blinking means that there is network traffic on the local
Ethernet network that is connected to the ETHERNET 1
10BASET port.
Any WAN
WAN
interface
Refer to the documentation that came with the WAN interface
interface
card card front panel
card.
LEDs
8.7 FRONT DISPLAY
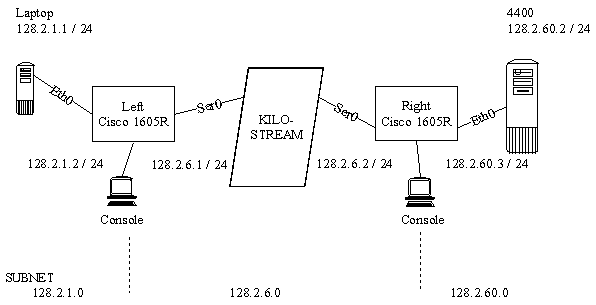
9 SAMPLE SET-UP
KILOSTREAM
9.1 Working example
A laptop with an Ethernet card is linked to a Right 4400 system via two Cisco 1605R
routers over
a 64k bandwidth Kilostream line. See Network Diagram for details.
For this example LEFT is the remote end and RIGHT is the system end.
Prerequisites:
2 Cisco 1605R routers.
2 Blue Console rollover cables with both 9pin and 25pin to RJ45 adapters [ supplied with
Routers ].
1 H type cable for use with a VDU.
1 VDU or PC to use as a console to set-up the routers.
2 Serial WAN cards for the Routers.
2 DTE Serial to Kilostream cables.
1 working Kilostream Line or Simulator.
1 Ethernet crossover cable [MIDI X] to link between Laptop and Left Router Ethernet 0
port.
1 Ethernet crossover cable [MIDI X] to link between Host and Right Router Ethernet 0 port.
A short RJ45 crossover cable [MIDI X] is supplied with the Router.
EDP cable type JP is an RJ45 crossover cable [MIDI X].
10 EDP
Cables & Adaptors for Cisco Use
KK Kilostream to NTU
KP Cisco Router Adaptor marked 29-0881-01 2620 Aux to Modem
KQ Cisco Router Adaptor marked 74-0495-01 Cisco router to PC Com
KR Cisco Router Adaptor marked TERMINAL CAB-500 DIF 29-0810-10
1605/2620 Aux to VDU
KS Cisco Rollover RJ45 to RJ45 1 to 8----8 to 1
KU Cisco Console port to VDU
KV Cisco Console port to PC
11 LEFT
ROUTER SETUP - KILOSTREAM
11.1 Connect the Blue Console
cable to the Cisco 1605R Router Console port at the rear of the Router
in the middle; and to the PC or VDU.
For a PC with a 9 pin male connector on Com1 port use the 9 pin female to RJ45 adapter.
[ See additional notes on HyperTerminal emulation program for PC use. ]
11.2 For a VDU with a 25 pin
female connector use the 25 pin female to RJ45 adapter plus an H
type cable to gender change.
Ensure settings of 9600, 8, N with VT100 emulation are used for Console access.
11.3 Power on the Router and
observe the LEDS and Console messages for about two minutes whilst
the router loads it’s software. The following lights should be lit on the front
panel:
SYSTEM PWR Green The router is turned on, and DC power is being supplied.
SYSTEM OK Green Blinks during the boot cycle Steady when
successfully booted.
ETH0 ACT Green Random flashes as data is being
sent via the first Ethernet LAN.
WIC CD/B1 Green lit on an active line i.e. carrier
detect.
11.4 On the rear panel the
following lights should be lit:
LNK at 10BASE T Ethernet0 If an active network
cable is fitted.
OK WIC
If the WAN Interface Card is correctly installed.
OK FLASH PC CARD
If the Flash Pc Card is correctly installed.
CONN on SERIAL WAN CARD If an active Kilostream is connected.
Access the console by pressing the return key.
If the Router has not been configured before the following Messages will appear:
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog [ yes/no]: yes
Would you like to enter basic management setup [ yes/no]: no
Display interface summary press <CR> key
Configuring global parameters:
Enter host name [Router]: type in the name of the Router i.e. Left
11.5 The enable secret is a password
used to protect access to privileged EXEC and configuration
modes.
This password, after entered becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Enter enable secret:
Note The EDP preferred enable secret password is currently qq
Note The password is case sensitive.
Enter enable password :
Note The EDP preferred enable password is currently q
Note The password is case sensitive.
Enter virtual terminal password:
Note The EDP preferred virtual terminal password is currently q
Note The password is case sensitive.
11.6 Configure SNMP Network Management no
Configure IP
no
Configure bridging
no
Configure Serial0 interface
no
Configure Ethernet 0 interface
no
Configure Ethernet 1 interface
no
Now take option 2
save this configuration to nvram and exit.
Building configuration…
Press <CR> key, press <CR> key again and login to the router
11.7 Note default settings appear in square
brackets [ ] .
Use Ctrl + C to abort the configuration at any time.
11.8 The Prompt should now change to Left>
If the Router has been configured before the following Messages will appear:
Router con0 is now available
Press RETURN to get started.
11.9 Set the Left Router configuration first
from the Left> prompt.
Type in en to access the EXEC level
Type in the password [qq] when prompted
Prompt changes to Left# [ in some character sets a British pound sign £ will be shown
i.e. Left£ ]
Show commands work at this level. The command show —
interfaces will display interfaces
settings.
This command could be shortened to sh — int .
The command sh — running displays the current
configuration whereas sh — startup displays the
configuration used during bootup. Therefore at the end of configuring a Router the amended
configuration needs to be copied from running to startup [ see details later ].
Use the <CR> key to move down a line at a time or the Spacebar to move
down a page at a time.
The up and down arrow keys can be used to access previous commands from the stack.
A question mark ? shows the commands present at the current level.
A command followed by a space then ? shows the command options available.
11.10 Type in clock — set hh:mm:ss
— dd — month —
yyyy to configure the routers clock .
Type in config — term to configure the router via the
console.
The prompt will now be Left(config)#
Type in service — timestamps —
log — datetime
The command hostname — Left would change the name of
the Router to Left.
Type in int — eth0 this selects the Ethernet0 interface
for configuration.
The prompt changes to Left(config-if)#
Before changing an interface parameter the interface must be shutdown.
Type in shutdown or shut this changes the Ethernet0 interface state from up
to admin .
11.11 Note a Cisco 1605R router by default has two
Ethernet interfaces eth0 and eth1.
In this working example only eth0 is used so eth1 should remain in admin i.e. shutdown.
11.12 Set the IP address and subnet mask for eth0 as
follows:
For the working example type in ip — address — 128.2.1.2 — 255.255.255.0
Note 255.255.255.0 is also known as a 24bit subnet mask often shown as /24
Type in ip address xxx.yyy.zzz.www — aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
Where xxx.yyy.zzz.www is the desired ip address
Where aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd is the desired subnet mask.
Type in no — shut this changes the Ethernet0 interface
state from admin to up.
Type in int — ser0 this selects the Serial0 WAN
interface for configuration.
Before changing an interface parameter the interface must be shutdown.
Type in shutdown or shut this changes the ser0 interface state from up
to admin .
11.13 Set the IP address and subnet mask for ser0 as
follows:
For the working example type in ip — address — 128.2.6.1 — 255.255.255.0
The Kilostream protocol needs to be set
Type in encapsulation — ppp This sets the protocol to
ppp .
The Kilostream bandwidth needs to be set
Type in bandwidth — 64 This sets the Kilostream
bandwidth to 64k
11.14 Type in no — shut
this changes the Serial0 WAN interface state from admin to up.
Type in exit at the prompt Left(config-if)#
This moves back up one level and the prompt changes to Left(config)#
Now the IP routes or routing information needs to be added to the Cisco 1605R router.
There must be one for each subnet plus the gateway of last resort.
Type in ip routing
For the working example type in the following ip routes :
Type in ip — route — 128.2.1.0 — 255.255.255.0 — eth0 This
describes the left subnet
Type in ip — route — 128.2.6.0 — 255.255.255.0 — ser0
This describes the middle subnet
Type in ip — route — 128.2.60.0
— 255.255.255.0 — 128.2.6.2
This describes the right subnet
Type in ip — route — 0.0.0.0 — 0.0.0.0 — ser0
This describes the gateway of last resort.
Type in exit at the prompt Left(config)#
This moves back up one level and the prompt changes to Left#
11.15 The command sh — int
will display interfaces settings - confirm the IP addresses are correct.
The command sh — running will display all the router
settings - confirm the IP routes etc are correct.
Now type in copy — running —
startup and hit <CR> again at the Destination filename
[startup-config-]?
Now displays Building configuration . . .
[OK]
Left#
The settings have now been saved and the configuration of Left router is complete
12 RIGHT ROUTER
SETUP – KILOSTREAM
12.1 Now complete the settings for
Right Router by connecting directly to the Right router Console port
[ see LEFT SETUP for details ]
12.2 Access the console by pressing the
<CR> key.
If the Router has not been configured before the following Messages will appear:
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog [ yes/no]: yes
Would you like to enter basic management setup [ yes/no]: no
Display interface summary press <CR> key
Configuring global parameters:
Enter host name [Router]: type in the name of the Router i.e. Right
12.3 The enable secret is a password used to
protect access to privileged EXEC and configuration
modes.
This password, after entered becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Enter enable secret:
Note The EDP preferred enable secret password is currently qq
Note The password is case sensitive.
Enter enable password :
Note The EDP preferred enable password is currently q
Note The password is case sensitive.
Enter virtual terminal password:
Note The EDP preferred virtual terminal password is currently q
Note The password is case sensitive.
12.4 Configure SNMP Network Management
no
Configure IP
no
Configure bridging
no
Configure Serial0 interface
no
Configure Ethernet 0 interface
no
Configure Ethernet 1 interface
no
Now take option 2
save this configuration to nvram and exit.
Building configuration…
Press <CR> key, press return key again and login to the router
12.5 Note default settings appear in square
brackets [ ] .
Use Ctrl + C to abort the configuration at any time.
12.6 The Prompt should now change to Right>
If the Router has been configured before the following Messages will appear:
Router con0 is now available
Press RETURN to get started.
12.7 Type in en to access the EXEC
level
Type in the password [qq] when prompted
Prompt changes to Right# [ in some character sets a British pound sign £ will be
shown i.e. Right£ ]
Show commands work at this level. The command show —
interfaces will display interfaces settings.
This command could be shortened to sh — int .
The command sh — running displays the current
configuration whereas sh — startup displays
the
configuration used during bootup. Therefore at the end of configuring a Router, the
amended
configuration needs to be copied from running to startup [ see details later ].
Use the <CR> key to move down a line at a time or the Spacebar to move down a
page at a time.
The up and down arrow keys can be used to access previous commands from the stack.
A
question mark ? shows the commands present at the current level.
A
command followed by a space then ? shows the command options available.
12.8 Type in clock —
set hh:mm:ss — dd — month — yyyy to configure the routers clock .
Type in config — term to configure the router via the
console.
The prompt will now be Right(config)#
Type in service — timestamps —
log — datetime
The command hostname — Right would change the name of
the Router to Right.
Type in int — eth0 this selects the Ethernet0 interface
for configuration.
The
prompt changes to Right(config-if)#
Before
changing an interface parameter the interface must be shutdown.
Type in shutdown
or shut this changes the Ethernet0 interface state from up to admin .
12.9 Note a Cisco 1605R router by default has two
Ethernet interfaces eth0 and eth1.
In this
working example only eth0 is used so eth1 should remain in admin i.e. shutdown.
12.10 Set the IP address and subnet mask for eth0 as follows:
For the
working example type in ip — address —
128.2.60.3 — 255.255.255.0
Note 255.255.255.0
is also known as a 24bit subnet mask often shown as /24
Type in ip
address xxx.yyy.zzz.www — aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
Where xxx.yyy.zzz.www
is the desired ip address
Where aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
is the desired subnet mask.
Type in no
— shut this changes the Ethernet0 interface state from admin
to up.
Type in int
— ser0 this selects the Serial0 WAN interface for
configuration.
Before
changing an interface parameter the interface must be shutdown.
Type in shutdown
or shut this changes the ser0 interface state from up to admin .
12.11 Set the IP address and subnet mask for ser0 as follows:
For the
working example type in ip — address —
128.2.6.2 — 255.255.255.0
The Kilostream
protocol needs to be set
Type in encapsulation
— ppp This sets the protocol to ppp .
The Kilostream
bandwidth needs to be set
Type in bandwidth
— 64 This sets the Kilostream bandwidth to 64k
12.12 Type in no — shut this changes the
Serial0 WAN interface state from admin to up.
Type in exit
at the prompt Right(config-if)#
This moves
back up one level and the prompt changes to Right(config)#
Now the IP
routes or routing information needs to be added to the Cisco 1605R router.
There must be
one for each subnet plus the gateway of last resort.
Type in ip
routing
For the
working example type in the following ip routes :
Type in ip — route — 128.2.60.0 —
255.255.255.0 — eth0
This describes the right subnet
Type in ip — route — 128.2.6.0 —
255.255.255.0 — ser0
This describes the middle subnet
Type in ip — route — 128.2.1.0 —
255.255.255.0 — 128.2.6.1
This describes the left subnet
Type in ip — route — 0.0.0.0 —
0.0.0.0 — ser0
This describes the gateway of last resort.
12.13 Type in exit at the prompt Right(config)#
This moves
back up one level and the prompt changes to Right#
The command sh
— int will display interfaces settings - confirm the IP
addresses are correct.
The command sh
— running will display all the router settings - confirm
the IP routes etc are correct.
Now type in copy
— running — startup and hit
enter again at the Destination filename
[startup-config-]?
Now displays Building
configuration . . .
[OK]
Right#
12.14 The settings have been saved and the configuration of Right router is
complete.
12.15 The link should now be up and running with a complete data path from Laptop
to 4400 computer.
12.16 The command telnet — 128.2.60.2 from the
laptop should now access the 4400 computer. .
Providing that the
Gateway of 128.2.1.2 has been set-up on the laptop, and on the system a route
to the laptop network
has been established as follows:
usr/sbin/route — add — -net —
128.2.1.0 — 128.2.60.3
12.17 You should now be able to ping all ip addresses in this working
example.
You should also be able
to telnet all Cisco router IP addresses in this working example
[ Note you cannot
telnet the subnet addresses ] .
13 SAMPLE SET-UP ISDN
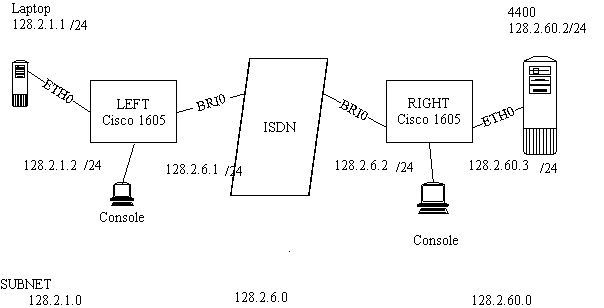
13.1 Working example
A laptop with an
Ethernet card is linked to a remote 4400 system via two Cisco 1605R routers over
a 64k bandwidth ISDN
line. See Network Diagram ISDN for details.
For this example
Left is the remote end and Right is the main host end.
13.2 Prerequisites:
2 Cisco 1605R
routers with associated power supplies including 13Amp mains plugs fitted.
2 Blue Console
cables with both 9pin and 25pin to RJ45 adapters [ supplied with Routers ]
1 H Type cable for
use with a VDU.
1 VDU or PC to use
as a console to set-up the routers.
2 ISDN BRI cards for
the Routers.
2 RJ45 Patch cables
to link Routers to ISDN line or Simulator.
1 working ISDN line
or Simulator.
1 Ethernet crossover
cable [MIDI X] to link between Laptop and Left Router Ethernet 0 port.
1 Ethernet crossover
cable [MIDI X] to link between Host and Right Router Ethernet 0 port.
Note
A short RJ45 crossover cable [MIDI X] is supplied with the Router.
EDP cable type JP is an RJ45 crossover cable [MIDI X].
EDP cable type JF is an RJ45 straight cable [MIDI].
14 LEFT ROUTER SETUP – ISDN
14.1 Connect one end of the Blue Console cable to the Cisco 1605R
Router Console port at the rear of
the Router in the
middle. Connect the other end of the Blue Console cable to the PC or VDU.
For a PC with a 9
pin male connector on Com1 port use the 9 pin female to RJ45 adapter.
[ See additional
notes on HyperTerminal emulation program for PC use. ]
14.2 For a Vdu with a 25 pin female connector use the 25 pin female
to RJ45 adapter plus an H type
cable to gender change.
Ensure settings of 9600,
8, N with VT100 emulation are used for Console access.
14.3 Power on the router and observe the leds and Console messages
for two mins whilst the router loads
it’s software. The
following lights should be lit on the front panel:
SYSTEM PWR
Green
The router is turned on, and DC power is
being supplied.
SYSTEM OK
Green
Blinks during the boot cycle Steady when
successfully booted.
ETH0 ACT
Green Random flashes as data is being
sent via the first Ethernet LAN.
WIC CD/B1
Green
lit on an active line i.e. carrier
detect.
14.4 On the rear panel the following lights should be lit:
LNK at 10BASE
T Ethernet0 If an active network cable is
fitted.
OK WIC
If the WAN Interface Card is correctly installed.
OK FLASH PC CARD
If the Flash Pc Card is correctly installed.
OK on ISDN
WAN CARD If a
connection is made to live ISDN
B1 on ISDN
WAN CARD If
an active call is connected.
Access the console
by pressing the return key.
If the Router has
not been configured before the following Messages will appear:
--- System
Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to
enter the initial configuration dialog [ yes/no]: yes
Would you like to
enter basic management setup [ yes/no]: no
Display interface
summary press <CR> key
Configuring global
parameters:
Enter host name
[Router]: type in the name of the Router i.e. Left
14.5 The enable secret is a password used to protect access to
privileged EXEC and configuration modes.
This password, after
entered becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Enter enable secret:
Note The EDP
preferred enable secret password is currently qq
Note The password
is case sensitive.
Enter enable
password :
Note The EDP
preferred enable password is currently q
Note The password
is case sensitive.
Enter virtual
terminal password:
Note The EDP
preferred virtual terminal password is currently q
Note The password
is case sensitive.
14.6 Configure SNMP no
Configure IP
no
Configure bridging
no
ISDN SWITCH TYPE 4
( selects net3 - note this is not the default )
Configure eth0
no
Configure eth1
no
Now take option 2 save
this configuration to nvram and exit
Press <CR>
key and login to the router.
14.7 Note default settings appear in square brackets [ ] .
Use Ctrl + C
to abort the configuration at any time.
14.8 The Prompt should now change to Left>
If the Router has
been configured before the following Messages will appear:
Router con0 is now
available
Press RETURN to get
started.
14.9 Set the Left Router configuration first from the Left>
prompt.
Type in en to
access the EXEC level
Type in the password
[qq] when prompted
Prompt changes to Left#
[ in some character sets a British pound sign £ will be shown i.e. Left£ ]
Show commands work
at this level. The command show — interfaces will
display interfaces settings.
This command could
be shortened to sh — int
.
The command sh — running displays the current configuration whereas sh — startup displays the
configuration used
during bootup. Therefore at the end of configuring a Router, the amended
configuration needs to
be copied from running to startup [ see details later ].
Use the <CR>
key to move down a line at a time or the Spacebar to move down a page at a time.
The up and down
arrow keys can be used to access previous commands from the stack.
A question mark ?
shows the commands present at the current level.
A command followed
by a space then ? shows the command options available.
14.10 Type in clock — set hh:mm:ss — dd — month —
yyyy to configure the routers clock.
Type in config — term to configure the router via the console.
The prompt will now
be Left(config)#
Type in service — timestamps — log —
datetime
The command hostname
— Left would change the name of the Router to Left.
Type in service — password-encryption
Type in username — Right — password —
Right
Type in int — eth0 this selects the Ethernet0 interface for configuration.
The prompt changes
to Left(config-if)#
Before changing an
interface parameter the interface must be shutdown.
Type in shutdown
or shut this changes the Ethernet0 interface state from up to admin .
14.11 Note a Cisco 1605R router by default has two Ethernet interfaces eth0 and
eth1.
In this ISDN working
example only eth0 is used so eth1 should remain in admin i.e. shutdown.
14.12 Set the IP address and subnet mask for eth0 as follows:
Type in ip — address — xxx.yyy.zzz.www — aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
For the working
example type in ip — address —
128.2.1.2 — 255.255.255.0
Where xxx.yyy.zzz.www
is the desired IP address.
Where aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
is the desired subnet mask.
Note 255.255.255.0
is also known as a 24bit subnet mask often shown as /24
Type in no — shut this changes the Ethernet0 interface state from admin to
up.
Type in exit The
prompt changes to Left(config)#
14.13 Type in int — bri0 this selects the ISDN
BRI interface for configuration.
The prompt will now
be Left(config-if)#
Before changing an
interface parameter the interface must be shutdown.
Type in shutdown
or shut this changes the bri0 interface state from up to admin .
Set the IP address
and subnet mask for bri0 as follows:
For the working
example type in ip — address —
128.2.6.1 — 255.255.255.0
The link protocol
needs to be set
Type in encapsulation
— ppp This sets the protocol to ppp .
Type in dialer — idle-timeout — 10 The idle timeout
is now set to 10 seconds to cut phone costs.
Type in dialer — string — 1111
Sets the ISDN
telephone number required to reach the other router, 1111.
Type in dialer — hold-queue — 10 Improves access
response
Type in
dialer-group — 1 Assigns the dialer
Type in ppp — authentication — pap Enables PAP
identification (security )
Type in ppp — pap — sent-username — Left — password —
0 — Left
Type in no — shut this changes the bri0 interface state from admin to
up.
Type in exit
at the prompt Left(config-if)#
This moves back up
one level and the prompt changes to Left(config)#
14.14 Now the IP routes or routing information needs to be added to the Cisco
1605R router.
Type in ip — routing Enables IP routing
There must be an ip
route for each subnet plus the gateway of last resort.
For the working
example type in the following ip routes :
Type in ip — route — 128.2.1.0 —
255.255.255.0 — eth0
This describes the left-hand subnet
Type in ip — route — 128.2.6.0 —
255.255.255.0 — bri0
This describes the middle subnet
Type in ip — route — 128.2.60.0 —
255.255.255.0 — 128.2.6.2
This describes the right-hand subnet
Type in ip — route — 0.0.0.0 —
0.0.0.0 — bri0
This describes the gateway of last resort.
Type in no — dialer-list — 1 This removes the
default dialer list
Type in dialer-list
— 1 — protocol —
ip — permit
This adds a new list for IP only.
Type in line — con — 0
Configures
console port
Prompt changes to Left(config-line)#
Type in password — q
Sets console port
password to q
Type in login
Enables console login
Type in exit
at the prompt Left(config-line)#
Type in exit
at the prompt Left(config)#
This moves back up
one level and the prompt changes to Left#
14.15 The command sh — int will display
interfaces settings - confirm the IP addresses are correct.
The command sh — running will display all the router settings - confirm the IP
routes etc are correct.
Now type in copy — running — startup and hit enter
again at the Destination filename
[startup-config-]?
Now displays Building
configuration . . .
[OK]
Left#
14.16 The settings have been saved and the configuration of Left router is now
complete.
15 RIGHT ROUTER SETUP – ISDN
15.1 Now input the settings for Right Router by connecting directly
into the Right router Console port
[ see LEFT ROUTER
SETUP for details ]
15.2 Access the console by pressing the return key.
If the Router has
not been configured before the following Messages will appear:
--- System
Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to
enter the initial configuration dialog [ yes/no]: yes
Would you like to
enter basic management setup [ yes/no]: no
Display interface
summary press <CR> key
Configuring global
parameters:
Enter host name
[Router]: type in the name of the Router i.e. Right
15.3 The enable secret is a password used to protect access to
privileged EXEC and configuration modes.
This password, after
entered becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Enter enable secret:
Note The EDP
preferred enable secret password is currently qq
Note The password
is case sensitive.
Enter enable
password :
Note The EDP
preferred enable password is currently q
Note The password
is case sensitive.
Enter virtual
terminal password:
Note The EDP
preferred virtual terminal password is currently q
Note The password
is case sensitive.
15.4 Configure SNMP
no
Configure IP
no
Configure bridging
no
ISDN SWITCH TYPE 4
( selects net3 - note this is not the default )
Configure eth0
no
Configure eth1
no
Now take option 2 save
settings to nvram and exit
Press <CR>
key and login to the router
15.5 Note default settings appear in square brackets [ ] .
Use Ctrl + C
to abort the configuration at any time.
15.6 The Prompt should now change to Right>
If the Router has
been configured before the following Messages will appear:
Router con0 is now
available
Press RETURN to get
started.
15.7 Set the Right Router configuration from the Right> prompt.
Type in en to
access the EXEC level
Type in the password
[qq] when prompted
Prompt changes to Right#
[ in some character sets a British pound sign £ will be shown i.e. Right£ ]
Show commands work
at this level. The command show — interfaces will
display interfaces settings.
This command could
be shortened to sh — int .
The command sh — running displays the current configuration whereas sh — startup displays the
configuration used
during bootup. Therefore at the end of configuring a Router the amended
configuration needs to
be copied from running to startup [ see details later ].
Use the <CR>
key to move down a line at a time or the Spacebar to move down a page at a time.
The up and down
arrow keys can be used to access previous commands from the stack.
A question mark ?
shows the commands present at the current level.
A command followed
by a space then ? shows the command options available.
15.8 Type in clock — set hh:mm:ss — dd — month —
yyyy to configure the routers clock .
Type in config — term to configure the router via the console.
The prompt will now
be Right(config)#
Type in service — timestamps — log —
datetime
The command hostname
— Right would change the name of the Router to Right.
Type in service — password-encryption Prevents passwords being readable when
displayed
Type in username — Left — password —
Left
This is required later
for CHAP identification
Type in int — eth0 this selects the Ethernet0 interface for configuration.
The prompt changes
to Right(config-if)#
Before changing an
interface parameter the interface must be shutdown.
Type in shutdown
or shut this changes the Ethernet0 interface state from up to admin .
15.9 Note a Cisco 1605R router by default has two Ethernet interfaces
eth0 and eth1.
In this ISDN working
example only eth0 is used so eth1 should remain in admin i.e. shutdown.
15.10 Set the IP address and subnet mask for eth0 as follows:
Type in ip — address — xxx.yyy.zzz.www — aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
For the working
example type in ip — address —
128.2.60.3 — 255.255.255.0
Where xxx.yyy.zzz.www
is the desired IP address.
Where aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
is the desired subnet mask.
Note 255.255.255.0
is also known as a 24bit subnet mask often shown as /24
Type in no — shut this changes the Ethernet0 interface state from admin to
up.
Type in exit The
prompt changes to Right(config)#
15.11 Type in int — bri0 this selects the ISDN
BRI interface for configuration.
The prompt will now
be Right(config-if)#
Before changing an
interface parameter the interface must be shutdown.
Type in shutdown
or shut this changes the bri0 interface state from up to admin .
Set the IP address
and subnet mask for bri0 as follows:
For the working
example type in ip — address —
128.2.6.2 — 255.255.255.0
The link protocol
needs to be set
Type in encapsulation
— ppp This sets the protocol to ppp .
Type in dialer — idle-timeout — 10
The idle timeout is now
set to 10 seconds to cut phone costs.
Type in dialer — string — 2222
Maps the IP address
of the router (Left) to the ISDN telephone number required to reach it (2222).
Type in dialer — hold-queue — 10 Improves access
response
Type in
dialer-group — 1 Assigns the dialer
Type in ppp — authentication — pap Enables PAP
identification (security )
Type in ppp — pap — sent-username — Right — password —
0 — Right
Type in no — shut this changes the bri0 interface state from admin to
up.
Type in exit
at the prompt Right(config-if)#
This moves back up
one level and the prompt changes to Right(config)#
15.12 Now the ip routes or routing information needs to be added to the Cisco
1605R router.
Type in ip — routing Enables IP routing
There must be an IP
route for each subnet plus the gateway of last resort.
For the working
example type in the following IP routes :
Type in ip — route — 128.2.60.0 —
255.255.255.0 — eth0
This describes the
right-hand subnet
Type in ip — route — 128.2.6.0 —
255.255.255.0 — bri0
This describes the
middle subnet
Type in ip — route — 128.2.1.0 —
255.255.255.0 — 128.2.6.1
This describes the
left-hand subnet
Type in ip — route — 0.0.0.0 —
0.0.0.0 — bri0
This describes the
gateway of last resort.
Type in no — dialer-list — 1 This removes the
default dialer list
Type in dialer-list
— 1 — protocol —
ip — permit This adds a new list
Type in line — con — 0 Configures console port
Prompt changes to Right(config-line)#
Type in password — q Sets console port password to q
Type in login
Enables console login
Type in exit
at the prompt Right(config-line)#
Type in exit
at the prompt Right(config)#
15.13 This moves back up one level and the prompt changes to Right#
The command sh — int will display interfaces settings - confirm the IP
addresses are correct.
The command sh — running will display all the router settings - confirm the IP
routes etc are correct.
Now type in copy — running — startup and hit enter
again at the Destination filename
[startup-config-]?
Now displays Building
configuration . . .
[OK]
Right#
15.14 The settings have now been saved and the configuration of Right router
is complete.
16 Final Tasks
16.1 The link should be able to be established with a temporary
data path from Laptop to 4400 computer.
The command telnet
— 128.2.60.2 from the laptop should now access the 4400
computer. Providing
that the Gateway of
128.2.1.2 has been set-up on the laptop, and on the system a route to the laptop
network has been
established as follows:
usr/sbin/route — add — -net —
128.2.1.0 — 128.2.60.3
16.2 When using numbered IP as in the example you will also need a
route to allow access to the router
Wan network.
usr/sbin/route — add — -net —
128.2.6.0 — 128.2.60.3
These will both be
required in the /etc/inet/gateways.eth file for access after a reboot.
16.3 You should now be able to ping all IP addresses in the
working example .
You should also be
able to telnet all Cisco router IP addresses in the working example [ Note you
cannot telnet
the subnet addresses ] .
Return to
Index