 Other Information You May Need
Other Information You May Need
 Accessing System Features During Startup
Accessing System Features During Startup
 Front-Panel Features and Indicators
Front-Panel Features and Indicators
Dell™ PowerEdge™ 2900 Systems Hardware Owner's Manual
|
|
This section describes the physical, firmware, and software interface features that provide and ensure the essential functioning of your system. The physical connectors on your system's front and back panels provide convenient connectivity and system expansion capability. The system firmware, applications, and operating systems monitor the system and component status and alert you when a problem arises. System conditions can be reported by any of the following:
This section describes each type of message, lists the possible causes, and provides steps to resolve any problems indicated by a message. The system indicators and features are illustrated in this section.
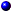
Figure 1-1 shows the rack and tower versions of your system. The illustrations in this document are based on the rack version, unless otherwise indicated.
Figure 1-1. Tower and Rack-Mount Orientations
|
1 |
system control panel (rack) |
2 |
system control panel (tower) |

|
CAUTION: The Product Information Guide provides important safety and regulatory information. Warranty information may be included within this document or as a separate document. |

|
NOTE: Always check for updates on support.dell.com and read the updates first because they often supersede information in other documents. |
Table 1-1 describes keystrokes that may be entered during startup to access system features. If your operating system begins to load before you enter the keystroke, allow the system to finish booting, and then restart your system and try again.
Table 1-1. Keystrokes for Accessing System Features
|
Keystroke |
Description |
|---|---|
<F2> | Enters the System Setup program. See Using the System Setup Program. |
<F10> | Opens the utility partition, allowing you to run the system diagnostics. See Running the System Diagnostics. |
<Ctrl+E> | Enters the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) Management Utility, which allows access to the system event log (SEL). See the BMC User's Guide for more information on setup and use of BMC. |
<Ctrl+C> | Enters the SAS Configuration Utility. See your SAS adapter User's Guide for more information. |
<Ctrl+R> | Enters the RAID configuration utility, which allows you to configure an optional RAID card. For more information, see the documentation for your RAID card. |
<Ctrl+S> | Option is displayed only if you have PXE support enabled through the System Setup Program (see Integrated Devices Screen). This keystroke allows you to configure NIC settings for PXE boot. For more information, see the documentation for your integrated NIC. |
<Ctrl+D> | If you have the optional Dell Remote Access Controller (DRAC), this keystroke allows access to selected DRAC configuration settings. See the DRAC User's Guide for more information on setup and use of DRAC. |
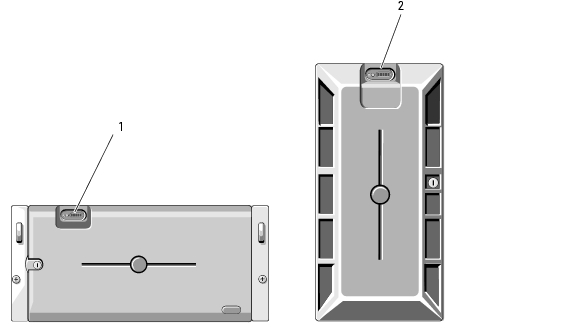
Figure 1-2 shows the controls, indicators, and connectors located behind the optional rack bezel on the system's front panel. Table 1-2 provides component descriptions.
Figure 1-2. Front-Panel Features and Indicators
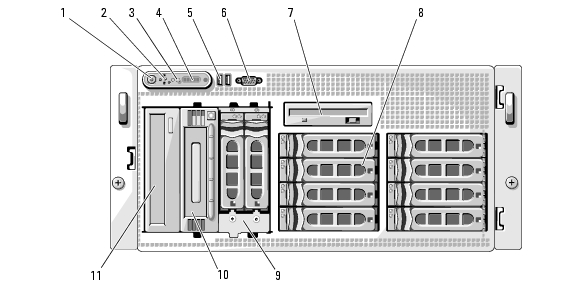
Table 1-2. Front-Panel Components
The hard-drive carriers have two indicators—the drive-activity indicator and the drive-status indicator. See Figure 1-3. In RAID configurations, the drive-status indicator lights to indicate the status of the drive. In non-RAID configurations, only the drive-activity indicator lights; the drive-status indicator is off.
Figure 1-3. Hard-Drive Indicators
|
1 |
drive-status indicator (green and amber) |
2 |
green drive-activity indicator |
Table 1-3 lists the drive indicator patterns for RAID hard drives. Different patterns are displayed as drive events occur in the system. For example, if a hard drive fails, the "drive failed" pattern appears. After the drive is selected for removal, the "drive being prepared for removal" pattern appears, followed by the "drive ready for insertion or removal" pattern. After the replacement drive is installed, the "drive being prepared for operation" pattern appears, followed by the "drive online" pattern.

|
NOTE: For non-RAID configurations, only the drive-activity indicator is active. The drive-status indicator is off. |
Table 1-3. Hard-Drive Indicator Patterns for RAID
Figure 1-4 shows the controls, indicators, and connectors located on the system's back panel.
Figure 1-4. Back-Panel Features and Indicators
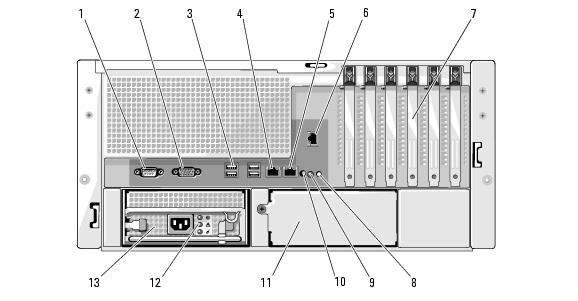
|
1 |
serial connector |
2 |
video connector |
3 |
USB connectors (4) |
|
4 |
NIC1 connector |
5 |
NIC2 connector |
6 |
remote access connector (optional) |
|
7 |
expansion-card slots (6) |
8 |
system status indicator |
9 |
system identification button |
|
10 |
system status indicator connector |
11 |
power supply 2 (optional) |
12 |
power supply status indicators |
|
13 |
power supply 1 |
|
|
|
|
When connecting external devices to your system, follow these guidelines:
See Using the System Setup Program for information about enabling, disabling, and configuring I/O ports and connectors.
The power button on the front panel controls the power input to the system's power supplies. The power indicator lights green when the system is on.
The indicators on the optional redundant power supplies show whether power is present or whether a power fault has occurred (see Table 1-4 and Figure 1-5).
Table 1-4. Redundant Power Supply Indicators
Figure 1-5. Redundant Power Supply Indicators

|
1 |
power supply status |
2 |
power supply fault |
3 |
AC line status |
Each NIC on the back panel has an indicator that provides information on network activity and link status. See Figure 1-6. Table 1-5 lists the NIC indicator codes.
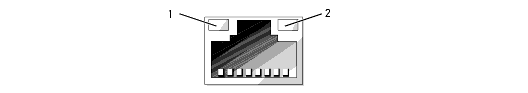
|
1 |
link indicator |
2 |
activity indicator |
Table 1-5. NIC Indicator Codes
The system's control panel LCD provides status messages to signify when the system is operating correctly or when the system needs attention. The LCD lights blue to indicate a normal operating condition and lights amber to indicate an error condition. The LCD scrolls a message that includes a status code followed by descriptive text.
Table 1-6 lists the LCD status messages that can occur and the probable cause for each message. The LCD messages refer to events recorded in the system event log (SEL). For information on the SEL and configuring system management settings, see the systems management software documentation.

|
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge. |

|
NOTE: If your system fails to boot, press the System ID button for at least five seconds until an error code appears on the LCD. Record the code, then see Getting Help. |
Table 1-6. LCD Status Messages
|
Code |
Text |
Causes |
Corrective Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
|
N/A |
SYSTEM NAME | A 62-character string that can be defined by the user in the System Setup program. The SYSTEM NAME displays under the following conditions: | This message is for information only. You can change the system string in the System Setup program. See Using the System Setup Program. |
|
E1000 |
FAILSAFE, Call Support |
| See Getting Help. |
|
E1114 |
Temp Ambient | Ambient system temperature is out of acceptable range. | |
|
E1116 |
Temp Memory | Memory has exceeded acceptable temperature and has been disabled to prevent damage to the components. | |
|
E1210 |
CMOS Batt | CMOS battery is missing, or the voltage is out of acceptable range. | |
|
E1211 |
ROMB Batt | RAID battery is either missing, bad, or unable to recharge due to thermal issues. | Reseat the RAID battery. See Replacing the SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card Battery, and Troubleshooting System Cooling Problems. |
|
E12nn |
XX PwrGd | Specified voltage regulator has failed. | See Getting Help. |
|
E1229 |
CPU # VCORE | Processor # VCORE voltage regulator has failed. | See Getting Help. |
|
E1310 |
RPM Fan ## | RPM of specified cooling fan is out of acceptable operating range. | |
|
E1313 |
Fan Redundancy | The system is no longer fan-redundant. Another fan failure will put the system at risk of over-heating. | Check control panel LCD for additional scrolling messages. See Troubleshooting System Cooling Problems. |
|
E1410 |
CPU # IERR | Specified microprocessor is reporting a system error. | See your system's Information Update Tech Sheet located on support.dell.com for the most current system information. If the problem persists, see Getting Help. |
|
E1414 |
CPU # Thermtrip | Specified microprocessor is out of acceptable temperature range and has halted operation. | See Troubleshooting System Cooling Problems. If the problem persists, ensure that the microprocessor heat sinks are properly installed. See Troubleshooting the Microprocessors. NOTE: The LCD continues to display this message until the system's power cord is disconnected and reconnected to the AC power source, or the SEL is cleared using either Server Assistant or the BMC Management Utility. See the Dell OpenManage Baseboard Management Controller User's Guide for information about these utilities. |
|
E1418 |
CPU # Presence | Specified processor is missing or bad, and the system is in an unsupported configuration | |
|
E141C |
CPU Mismatch | Processors are in a configuration unsupported by Dell. | Ensure that your processors match and conform to the type described in the Microprocessor Technical Specifications outlined in your system's Getting Started Guide. |
|
E141F |
CPU Protocol | The system BIOS has reported a processor protocol error. | See Getting Help. |
|
E1420 |
CPU Bus PERR | The system BIOS has reported a processor bus parity error. | See Getting Help. |
|
E1421 |
CPU Init | The system BIOS has reported a processor initialization error. | See Getting Help. |
|
E1422 |
CPU Machine Chk | The system BIOS has reported a machine check error. | See Getting Help. |
|
E1610 |
PS # Missing | No power is available from the specified power supply; specified power supply is improperly installed or faulty. | |
|
E1614 |
PS # Status | No power is available from the specified power supply; specified power supply is improperly installed or faulty. | |
|
E1618 |
PS # Predictive | Power supply voltage is out of acceptable range; specified power supply is improperly installed or faulty. | |
|
E161C |
PS # Input Lost | Power source for specified power supply is unavailable, or out of acceptable range | Check the AC power source for the specified power supply. If problem persists, see Troubleshooting Power Supplies. |
|
E1620 |
PS # Input Range | Power source for specified power supply is unavailable, or out of acceptable range | Check the AC power source for the specified power supply. If problem persists, see Troubleshooting Power Supplies. |
|
E1624 |
PS Redundancy | The power supply subsystem is no longer redundant. If the last supply fails, the system will go down. | |
|
E1710 |
I/O Channel Chk | The system BIOS has reported an I/O channel check error. | See Getting Help. |
|
E1711 |
PCI PERR B## D## F## PCI PERR Slot # | The system BIOS has reported a PCI parity error on a component that resides in PCI configuration space at bus ##, device ##, function ##. The system BIOS has reported a PCI parity error on a component that resides in PCI slot #. | Remove and reseat the PCI expansion cards. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting Expansion Cards. If the problem persists, the system board is faulty. See Getting Help. |
|
E1712 |
PCI SERR B## D## F## PCI SERR Slot # | The system BIOS has reported a PCI system error on a component that resides in PCI configuration space at buss ##, device ##, function ##. The system BIOS has reported a PCI system error on a component that resides in slot #. | Remove and reseat the PCI expansion cards. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting Expansion Cards. If the problem persists, the system board is faulty. See Getting Help. |
|
E1714 |
Unknown Err | The system BIOS has determined that there has been an error in the system, but is unable to determine its origin. | See Getting Help. |
|
E171F |
PCIE Fatal Err B## D## F## PCIE Fatal Err Slot # | The system BIOS has reported a PCIe fatal error on a component that resides in PCI configuration space at bus ##, device ##, function ##. The system BIOS has reported a PCIe fatal error on a component that resides in slot #. | Remove and reseat the PCI expansion cards. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting Expansion Cards. If the problem persists, the system board is faulty. See Getting Help. |
|
E1810 |
HDD ## Fault | The SAS subsystem has determined that hard drive ## has experienced a fault. | |
|
E1811 |
HDD ## Rbld Abrt | The specified hard drive has experienced a rebuild abort. | See Troubleshooting a Hard Drive. If the problem persists, see your RAID documentation. |
|
E1812 |
HDD ## Removed | The specified hard drive has been removed from the system. | Information only. |
|
E1913 |
CPU & Firmware Mismatch | The BMC firmware does not support the CPU. | Update to the latest BMC firmware. See the BMC User's Guide for more information on setup and use of BMC. |
|
E1A10 |
PBD Pwr Cable | The power distribution board power cable is unseated, missing, or bad. | Ensure that the power distribution board power cable is seated properly. If the problem persists, replace the power distribution board power cable. See Installing the Power Distribution Board. |
|
E1A14 |
SAS Cable A | SAS cable A is unseated, missing, or bad. | Check the cable connection to the SAS backplane. See Cabling the SAS Backplane Boards. |
|
E1A15 |
SAS Cable B | SAS cable B is unseated, missing, or bad. | Check the cable connection to the SAS backplane. See Cabling the SAS Backplane Boards. |
|
E1A16 |
SAS Cable FB | Flex bay SAS cable is unseated, missing, or bad. | Check the cable connection to the SAS backplane. See Cabling the SAS Backplane Boards. |
|
E1A17 |
Pwr Cable FB | Flex bay power cable is unseated, missing, or bad. | Check the power cable connection to the flex bay backplane. See Installing the 1x2 Flex Bay Drive Bracket. |
|
E1A18 |
PDB Ctrl Cable | The power distribution board control cable is unseated, missing, or bad. | Ensure that the power distribution board control cable is seated properly. If the problem persists, replace the power distribution board control cable. See Installing the Power Distribution Board. |
|
E2010 |
No Memory | No memory is installed in the system. | Install memory. See Memory. |
|
E2011 |
Mem Config Err | Memory detected, but is not configurable. Error detected during memory configuration. | |
|
E2012 |
Unusable Memory | Memory is configured, but not usable. Memory subsystem failure. | |
|
E2013 |
Shadow BIOS Fail | The system BIOS failed to copy its flash image into memory. | |
|
E2014 |
CMOS Fail | CMOS failure. CMOS RAM not functioning properly. | See Getting Help. |
|
E2015 |
DMA Controller | DMA controller failure. | See Getting Help. |
|
E2016 |
Int Controller | Interrupt controller failure. | See Getting Help. |
|
E2017 |
Timer Fail | Timer refresh failure. | See Getting Help. |
|
E2018 |
Prog Timer | Programmable interval timer error | See Getting Help. |
|
E2019 |
Parity Error | Parity error. | See Getting Help. |
|
E201A |
SIO Err | SIO failure. | See Getting Help. |
|
E201B |
Kybd Controller | Keyboard controller failure. | See Getting Help. |
|
E201C |
SMI Init | System management interrupt (SMI) initialization failure. | See Getting Help. |
|
E201D |
Shutdown Test | BIOS shutdown test failure. | See Getting Help. |
|
E201E |
POST Mem Test | BIOS POST memory test failure. | See Troubleshooting System Memory. If problem persists, see Getting Help. |
|
E201F |
DRAC Config | Dell remote access controller (DRAC) configuration failure. | Check screen for specific error messages. Ensure that DRAC cables and connectors are properly seated. If problem persists, see your DRAC documentation. |
|
E2020 |
CPU Config | CPU configuration failure. | Check screen for specific error messages. |
|
E2021 |
Memory Population | Incorrect memory configuration. Memory population order incorrect. | Check screen for specific error messages. See Troubleshooting System Memory. |
|
E2022 |
POST Fail | General failure after video. | Check screen for specific error messages. |
|
E2110 |
MBE DIMM ## & ## | One of the DIMMs in the set implicated by "## & ##" has had a memory multi-bit error (MBE). | |
|
E2111 |
SBE Log Disable DIMM ## | The system BIOS has disabled memory single-bit error (SBE) logging, and will not resume logging further SBEs until the system is rebooted. "##" represents the DIMM implicated by the BIOS. | |
|
E2112 |
Mem Spare DIMM ## | The system BIOS has spared the memory because it has determined that the memory had too many errors. "## & ##" represents the DIMM pair implicated by the BIOS. | |
|
E2113 |
Mem Mirror DIMM ## & ## | They system BIOS has disabled memory mirroring because it has determined that one half of the mirror has had too many errors. "## & ##" represents the DIMM pair implicated by the BIOS. | |
|
E2118 |
Fatal NB Mem CRC | One of the connections in the Fully Buffered DIMM (FBD) memory subsystem link on the Northbound side has failed. | |
|
E2119 |
Fatal SB Mem CRC | One of the connections in the FBD memory subsystem link on the Southbound side has failed. | |
|
I1910 |
Intrusion | System cover has been removed. | Information only. |
|
I1911 |
>3 ERRs Chk Log | LCD overflow message. A maximum of three error messages can display sequentially on the LCD. The fourth message displays as the standard overflow message. | Check the SEL for details on the events. |
|
I1912 |
SEL Full | System Event Log is full of events, and is unable to log any more events. | Clear the log by deleting event entries. |
|
W1228 |
ROMB Batt < 24hr | Warns predictively that the RAID battery has less than 24 hours of charge left. | Replace RAID battery. See Replacing the SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card Battery. |
|
NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the Glossary. | |||
When a single message appears on the status LCD, locate the code in Table 1-6 and perform the suggested corrective action. The code on the LCD can often specify a very precise fault condition that is easily corrected. For example, if the code E0780 MISSING CPU 1 appears, you know that a microprocessor is not installed in socket 1.
In contrast, you might be able to determine the problem if multiple related errors occur. For example, if you receive a series of messages indicating multiple voltage faults, you might determine that the problem is a failing power supply.
For faults associated with sensors, such as temperature, voltage, fans, and so on, the LCD message is automatically removed when that sensor returns to a normal state. For example, if temperature for a component goes out of range, the LCD displays the fault; when the temperature returns to the acceptable range, the message is removed from the LCD. For other faults, you must take action to remove the message from the display:
Either of the preceding actions will remove fault messages and return the status indicators and LCD colors to the normal state. Error messages will reappear under the following conditions:
System messages appear on the screen to notify you of a possible problem with the system. Table 1-7 lists the system messages that can occur and the probable cause and corrective action for each message.

|
NOTE: If you receive a system message that is not listed in Table 1-7, check the documentation for the application that is running when the message appears or the operating system's documentation for an explanation of the message and recommended action. |

|
CAUTION: Only trained service technicians are authorized to remove the system cover and access any of the components inside the system. See your Product Information Guide for complete information about safety precautions, working inside the computer, and protecting against electrostatic discharge. |
|
Message |
Causes |
Corrective Actions |
|---|---|---|
|
Alert! Redundant memory disabled! Memory configuration does not support redundant memory. | Installed memory modules are not the same type and size; faulty memory module(s). | Ensure that all memory modules are of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. See Memory. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting System Memory. |
|
Attempting to update Remote Configuration. Please wait... | Remote Configuration request has been detected and is being processed. | Wait until the process is complete. |
|
BIOS Update Attempt Failed! | Remote BIOS update attempt failed. | Retry the BIOS update. If problem persists, see Getting Help. |
|
Caution! NVRAM_CLR jumper is installed on system board. | NVRAM_CLR jumper is installed. CMOS has been cleared. | Remove the NVRAM_CLR jumper. See Figure 6-1 for jumper location. |
|
CPUs with different cache sizes detected! | Microprocessors with different cache sizes are installed. | Ensure that all microprocessors have the same cache size and that they are properly installed. See Microprocessor. |
|
Decreasing available memory | Faulty or improperly installed memory modules. | |
|
DIMM pairs must be matched in size, speed, and technology. The following DIMM pair is mismatched: DIMM x and DIMM y. | Mismatched or unmatched DIMMs installed; faulty or improperly seated memory module(s). | Ensure that all pairs of memory modules are of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. See Memory. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting System Memory. |
|
DIMMs must be populated in sequential order beginning with slot 1. The following DIMM is electrically isolated: DIMM x. | The specified DIMM is inaccessible to the system due to its location. DIMMs must be populated in sequential order, beginning with slot 1. | Populate 2, 4, 8, or 12 DIMMs sequentially beginning with slot 1. See Memory. |
|
DIMMs should be installed in pairs. Pairs must be matched in size, speed, and technology. | Mismatched or unmatched DIMMs installed; faulty or improperly seated memory module(s). The system will operate in a degraded mode with reduced ECC protection. Only memory installed in channel 0 will be accessible. | Ensure that all pairs of memory modules are of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. See Memory. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting System Memory. |
|
Dual-rank DIMM paired with Single-rank DIMM - The following DIMM/rank has been disabled by BIOS: DIMM x Rank y | Mismatched DIMMs installed; faulty memory module(s). The system has detected a dual-rank DIMM paired with a single-rank DIMM. The second rank of the dual-rank DIMM will be disabled. | Ensure that all pairs of memory modules are of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. See Memory. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting System Memory. |
|
Diskette drive n seek failure | Incorrect configuration settings in the System Setup program. | Run the System Setup program to correct the settings. See Using the System Setup Program. |
Faulty or improperly installed diskette drive. | Replace the diskette. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive. | |
Loose diskette drive interface cable, or loose power cable. | Reseat diskette drive interface cable, or power cable. See Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive. | |
|
Diskette read failure | Faulty or improperly inserted diskette. | Replace the diskette. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive. |
|
Diskette subsystem reset failed | Faulty or improperly installed diskette. | Replace the diskette. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive. |
|
Drive not ready | Diskette missing from or improperly inserted in diskette drive. | Replace the diskette. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive. |
|
Error: Incorrect memory configuration. DIMMs must be installed in pairs of matched memory size, speed, and technology. | Mismatched or unmatched DIMMs installed; faulty or improperly seated memory module(s). | Ensure that all pairs of memory modules are of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. See Memory. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting System Memory. |
|
Error: Memory failure detected. Memory size reduced. Replace the faulty DIMM as soon as possible. | Faulty or improperly seated memory module(s).
| |
|
!!*** Error: Remote Access Controller initialization failure*** RAC virtual USB devices may not be available... | Remote Access Controller initialization failure | Ensure that the Remote Access Controller is properly installed. See Installing a RAC Card. |
|
FBD training error: The following branch has been disabled: Branch x | The specified branch (channel pair) contains DIMMs that are incompatible with each other. | Ensure that only Dell-qualified memory is used. Dell recommends purchasing memory upgrade kits directly from www.dell.com or your Dell sales agent to ensure compatibility. |
|
Gate A20 failure | Faulty keyboard controller; faulty system board. | See Getting Help. |
|
General failure | The operating system is unable to carry out the command. | This message is usually followed by specific information. Note the information and take the appropriate action to resolve the problem. |
|
Invalid NVRAM configuration, Resource Re-allocated | System detected and corrected a resource conflict. | No action is required. |
|
Keyboard Controller failure | Faulty keyboard controller; faulty system board | See Getting Help. |
|
Manufacturing mode detected | System is in manufacturing mode. | Reboot to take the system out of manufacturing mode. |
|
MEMBIST failure - The following DIMM/rank has been disabled by BIOS: DIMM x Rank y | Faulty memory module(s).
| |
|
Memory address line failure at address, read value expecting value | Faulty or improperly installed memory modules. | |
|
Memory double word logic failure at address, read value expecting value | ||
|
Memory odd/even logic failure at address, read value expecting value | ||
|
Memory write/read failure at address, read value expecting value | ||
|
Memory tests terminated by keystroke. | POST memory test terminated by pressing the spacebar. | Information only. |
|
No boot device available | Faulty or missing optical/diskette drive subsystem, hard drive, or hard-drive subsystem, or no boot disk in drive A. | Use a bootable diskette, CD, or hard drive. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive, Troubleshooting an Optical Drive, and Troubleshooting a Hard Drive. See Using the System Setup Program for information about setting the order of boot devices. |
|
No boot sector on hard drive | Incorrect configuration settings in System Setup program, or no operating system on hard drive. | Check the hard-drive configuration settings in the System Setup program. See Using the System Setup Program. If necessary, install the operating system on your hard drive. See your operating system documentation. |
|
No timer tick interrupt | Faulty system board. | See Getting Help. |
|
Northbound merge error - The following DIMM has been disabled by BIOS: DIMM x | The specified DIMM was unable to establish a successful data link with the memory controller.
| |
|
Not a boot diskette | No operating system on diskette. | Use a bootable diskette. |
|
PCIe Degraded Link Width Error: Embedded Bus#nn/Dev#nn/Funcn Expected Link Width is n Actual Link Width is n | Faulty or improperly installed PCIe card in the specified slot. | Reseat the PCIe card in the specified slot number. See Expansion Cards. If the problem persists, see Getting Help. |
|
PCIe Degraded Link Width Error: Slot n Expected Link Width is n Actual Link Width is n | Faulty or improperly installed PCIe card in the specified slot. | Reseat the PCIe card in the specified slot number. See Expansion Cards. If the problem persists, see Getting Help. |
|
PCIe Training Error: Embedded Bus#nn/Dev#nn/Funcn PCIe Training Error: Slot n | Faulty or improperly installed PCIe card in the specified slot. | Reseat the PCIe card in the specified slot number. See Expansion Cards. If the problem persists, see Getting Help. |
|
PCI BIOS failed to install | PCI device BIOS (Option ROM) checksum failure is detected during shadowing. Loose cables to expansion card(s); faulty or improperly installed expansion card. | Reseat the expansion cards. Ensure that all appropriate cables are securely connected to the expansion cards. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting Expansion Cards. |
|
Plug & Play Configuration Error | Error encountered in initializing PCI device; faulty system board. | Install the NVRAM_CLR jumper and reboot the system. See Figure 6-1 for jumper location. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting Expansion Cards. |
|
Read fault Requested sector not found | The operating system cannot read from the diskette or hard drive, the system could not find a particular sector on the disk, or the requested sector is defective. | Replace the diskette. Ensure that the diskette and hard drive cables are properly connected. See Troubleshooting a USB Device, Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive, or Troubleshooting a Hard Drive for the appropriate drive(s) installed in your system. |
|
Remote configuration update attempt failed | System unable to process Remote Configuration request. | Retry Remote Configuration. |
|
ROM bad checksum = address | Expansion card improperly installed or faulty. | Reseat the expansion cards. Ensure that all appropriate cables are securely connected to the expansion cards. If the problem persists, see Troubleshooting Expansion Cards. |
|
Sector not found Seek error Seek operation failed | Faulty diskette or hard drive. | See Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive or Troubleshooting a Hard Drive for the appropriate drive(s) installed in your system. |
|
Shutdown failure | Shutdown test failure. | |
|
The amount of system memory has changed | Memory has been added or removed or a memory module may be faulty. | If memory has been added or removed, this message is informative and can be ignored. If memory has not been added or removed, check the SEL to determine if single-bit or multi-bit errors were detected and replace the faulty memory module. See Troubleshooting System Memory. |
|
The following DIMM pair is not compatible with the memory controller: DIMM x and DIMM y | The specified DIMM(s) are incompatible with the system. | Ensure that only Dell-qualified memory is used. Dell recommends purchasing memory upgrade kits directly from www.dell.com or your Dell sales agent to ensure compatibility. |
|
The following DIMMs are not compatible: DIMM x and DIMM y | The specified DIMM(s) are incompatible with the system. | Ensure that only ECC FBD1 memory is used. Dell recommends purchasing memory upgrade kits directly from www.dell.com or your Dell sales agent to ensure compatibility. |
|
Time-of-day clock stopped | Faulty battery or faulty chip. | |
|
Time-of-day not set - please run SETUP program | Incorrect Time or Date settings; faulty system battery. | Check the Time and Date settings. See Using the System Setup Program. If the problem persists, replace the system battery. See System Battery. |
|
Timer chip counter 2 failed | Faulty system board. | See Getting Help. |
|
Unsupported CPU combination Unsupported CPU stepping detected | Microprocessor(s) is not supported by the system. | Install a supported microprocessor or microprocessor combination. See Microprocessor. |
|
Utility partition not available | The <F10> key was pressed during POST, but no utility partition exists on the boot hard drive. | Create a utility partition on the boot hard drive. See the CDs that came with your system. |
|
Warning! No microcode update loaded for processor n | Microcode update failed. | Update the BIOS firmware. See Getting Help. |
|
Warning: Embedded RAID firmware is not present! | Embedded RAID firmware does not respond. | See the RAID controller documentation for information about installing or updating the RAID firmware. |
|
Warning: Embedded RAID error! | Embedded RAID firmware responds with an error. | See Troubleshooting a SAS or SAS RAID Controller Daughter Card. See the RAID controller documentation for information about installing or updating the RAID firmware. |
|
Warning: The current memory configuration is not optimal. Dell recommends a population of 2, 4, 8, or 12 DIMMs. DIMMs should be populated sequentially starting in slot 1. | System has detected a legal but non-optimal population of DIMMs (for example, 1 DIMM, 6 DIMMs, 4 DIMMs in slots 1, 2, 5, and 6, etc.). The system will run with all memory accessible but will experience sub-optimal performance. | Populate 2, 4, 8, or 12 DIMMs sequentially beginning with slot 1. See Memory. |
|
Write fault Write fault on selected drive | Faulty diskette, optical/diskette drive assembly, hard drive, or hard-drive subsystem. | See Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive, Troubleshooting an Optical Drive, or Troubleshooting a Hard Drive. |
|
NOTE: For the full name of an abbreviation or acronym used in this table, see the Glossary. | ||
A warning message alerts you to a possible problem and prompts you to respond before the system continues a task. For example, before you format a diskette, a message will warn you that you may lose all data on the diskette. Warning messages usually interrupt the task and require you to respond by typing y (yes) or n (no).

|
NOTE: Warning messages are generated by either the application or the operating system. For more information, see the documentation that accompanied the operating system or application. |
When you run system diagnostics, an error message may result. Diagnostic error messages are not covered in this section. Record the message on a copy of the Diagnostics Checklist in Getting Help, and then follow the instructions in that section for obtaining technical assistance.
Systems management software generates alert messages for your system. Alert messages include information, status, warning, and failure messages for drive, temperature, fan, and power conditions. For more information, see the systems management software documentation.