 System Status Indicators
System Status IndicatorsDell™ PowerEdge™ 6650 Systems Service Manual
 Front-Panel Indicators and Features
Front-Panel Indicators and Features
 Back-Panel Indicators and Features
Back-Panel Indicators and Features
 Expansion-Slot Indicator Codes
Expansion-Slot Indicator Codes
The system indicators and features are illustrated in Figure 3-1 through Figure 3-7. This section also describes each type of message and lists the possible causes and actions you can take to resolve any problems indicated by a message. To determine what type of message you have received, read the following subsections.
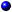
The system's bezel has an indictor that can represent system status when the bezel is installed (see Figure 3-1). The indicator identifies when the system is operating properly or when the system needs attention. The back-panel system status indicator functions the same as the bezel's status indicator. A flashing caution indicator light identifies a problem with power supply, system or power-supply fans, system temperature, hard drives, or expansion cards.
Table 3-1 lists the system's status indicator codes.
Figure 3-1. System Status Indicators
|
Bezel Indicators |
Back-Panel Indicator |
Indicator Code | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Status |
Caution | ||
Off | Off | Off | No power is available to the system, or the system is not powered on. |
On | Off | Blue | The system is operating normally. |
Off | Blinking | Amber blinking | The system has detected an error and requires attention. |
Blinking | Off | Blue blinking | The system is identifying itself. NOTE: Systems management software causes the status indicator to blink to identify a particular system. For more information, see the systems management software documentation. |
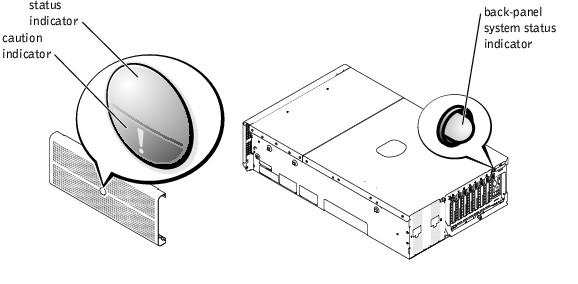
Additional indicators are located behind the bezel for system power and hard drives. The CD and diskette drives have green activity indicators. The front-panel LCD provides status information using an alphanumeric character display (see "LCD Status Messages"). See Figure 3-2 for the front-panel indicators and features.
Figure 3-2. Front-Panel Features
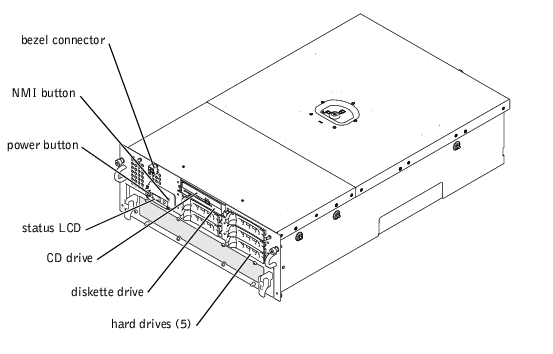
Figure 3-3 shows the back-panel features of the system.
Figure 3-3. Back-Panel Features
Each hard-drive carrier has two indicators: a busy indicator and a status indicator (see Figure 3-4). The indicators provide information on the status of the respective hard drive. Table 3-2 lists the drive indicator codes.
Figure 3-4. Hard-Drive Indicators
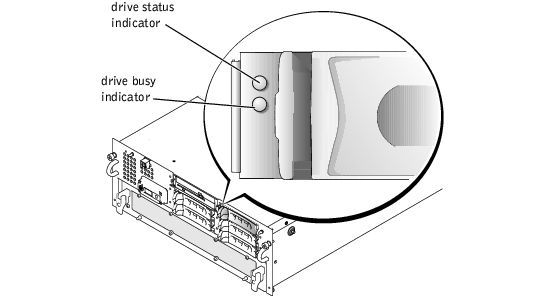
Table 3-2 lists the drive indicator codes. Different codes display as drive events occur in the system. For example, in the event of a hard-drive failure, the "drive fail" code appears. After the drive is selected for removal, the "drive being prepared for removal" code appears. After the replacement drive is installed, the "drive being prepared for operation" code appears, followed by "drive online" code.
|
Status Indicator |
Indicator Code |
|---|---|
Off | Drive bay empty, ready for insertion or removal |
Steady green | Drive being prepared for operation, drive online |
Blinks green four times per second | Identify drive |
Blinks green twice per second at equal intervals | Drive being prepared for removal |
Blinks green twice per second at unequal intervals | Drive rebuilding |
Blinks amber four times per second | Drive failed |
Blinks green, then amber, and then off, repeating this sequence every two seconds | Predicted failure for the drive |
Steady green | Drive online |
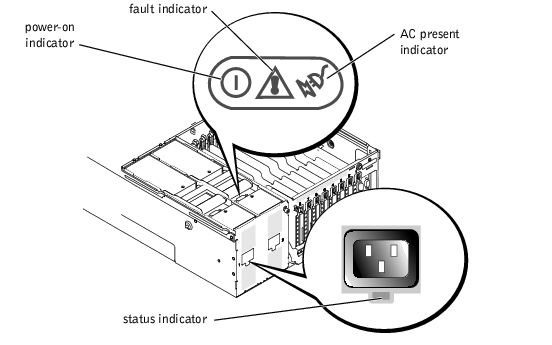
Each hot-pluggable power supply has three indicators that can provide information on power status, fault, and the presence of AC power (see Figure 3-5). Table 3-3 lists the power-supply indicator codes.
Figure 3-5. Power-Supply Indicators
|
Indicator |
Indicator Code |
|---|---|
Power-on | Green indicates that AC power is present at the power supply. |
Power-on | Green indicates that the power supply is operational. |
Fault | Red indicates a problem with the power supply (fan failure, voltage error, etc.). |
AC present | Green indicates that AC power is present at the power supply and that the system is connected to an AC source. |
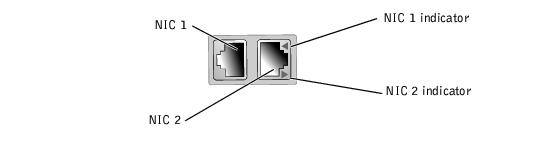
Each NIC has an indicator that provides information on network activity and link status (see Figure 3-6). Table 3-4 lists the NIC indicator codes.
|
Indicator |
Indicator Code |
|---|---|
Off | The NIC is not connected to the network. |
Green | The NIC is connected to a valid link partner. |
Amber blinking | Network data is being sent or received. |
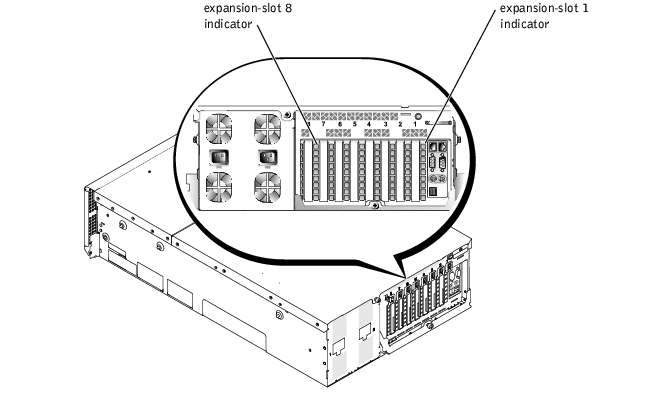
An indicator is located beside each PCI hot-pluggable expansion slot (see Figure 3-7). The indicators show through the back-panel vents. Table 3-5 lists the codes for these indicators.
Figure 3-7. Expansion-Slot Indicators
|
Indicator |
Indicator Code |
|---|---|
Off | Expansion-slot power is off. No action is required. |
Green | Expansion-slot power is on. No action is required. |
Green blinking fast | Expansion slot is being identified by an application program or driver. No action is required. |
Amber blinking slow | Expansion card is faulty or improperly installed, causing a problem with power supply to the card. |
Amber blinks twice, pauses, and then repeats the sequence | Expansion card of a slower operating speed was hot-plugged. If you are replacing an expansion card with a card of a slower operating speed, you must power down the system to install the replacement card. |
The system's bezel indictor can signify when the system is operating correctly or when the system needs attention (see Figure 3-1). When the bezel indicator signifies an error condition, open the bezel to see further information provided by the LCD.
The LCD can display two lines of alphanumeric characters. The display codes are presented in two color combinations:
Table 3-6 lists the LCD status messages that can occur and the probable cause for each message. The LCD messages refer to events recorded in the system event log (SEL). For information on the SEL and configuring system management settings, see the systems management software documentation found on the documentation CD that shipped with your system.
|
Line 1 |
Line 2 |
Causes |
Corrective Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
SYSTEM ID | SYSTEM NAME | SYSTEM ID is a unique name, 5 characters or less, defined by the user. SYSTEM NAME is a unique name, 16 characters or less, defined by the user. The system ID and name display under the following conditions:
| This message is for information only. You can change the system ID and name in the System Setup program. see "Using the System Setup Program." |
E0000 | OVRFLW CHECK LOG | LCD overflow message. A maximum of three error messages can display sequentially on the LCD. The fourth message displays as the standard overflow message. | Check the SEL for details on the events. |
E0119 | DRAC TEMP | Remote access card is out of acceptable temperature range. | Ensure that the system cooling fans are operating properly. If not, replace the faulty fan (see "Replacing a Cooling Fan"). If the problem persists, replace the remote access card (see "Expansion Cards"). |
E0119 | TEMP AMBIENT | Ambient system temperature is out of acceptable range. | |
E0119 | TEMP BP | Backplane board is out of acceptable temperature range. | Ensure that the system cooling fans are operating properly. If not, replace the faulty fan (see "Replacing a Cooling Fan"). Ensure that the power supply fault indicator is not lit. If lit, replace the power supply (see "Power Supplies"). If the power supplies are operating normally, replace the SCSI backplane board (see "Removing the SCSI Backplane"). |
E0119 | TEMP CPU n | Specified microprocessor is out of acceptable temperature range. | Ensure that the system cooling fans are operating properly. If not, replace the faulty fan (see "Replacing a Cooling Fan"). If the problem persists, ensure that the specified microprocessor heat sink(s) are properly installed (see "Adding or Replacing a Microprocessor"). |
E0119 | TEMP MEM n | Specified memory riser card is out of acceptable temperature range. | Ensure that the system cooling fans are operating properly. If not, replace the faulty fan (see "Replacing a Cooling Fan"). If the problem persists, replace the memory riser card (see "Removing a Memory Riser Card"). |
E0119 | TEMP SYSTEM | I/O riser card or I/O board is out of acceptable temperature range. | Replace the I/O riser card (see "Removing the I/O Riser Card"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Replacing the I/O Board"). |
E0212 | DRAC EXT POWER | Remote access card is out of acceptable voltage range; faulty or improperly installed power supply or remote access card. | Ensure that the power supply fault indicator is not lit. If lit, replace the power supply (see "Power Supplies"). If the problem persists, ensure that the remote access card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the remote access card (see "Expansion Cards"). |
E0212 | DRAC VOLT BATT | ||
E0212 | DRAC VOLT PCI | ||
E0212 | VOLT 3.3 | System power supply is out of acceptable voltage range; faulty or improperly installed power supply. | Ensure that the power supplies are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the power supply (see "Power Supplies"). |
E0212 | VOLT 5 | 5-V VRM is out of acceptable voltage range; faulty or improperly installed 5-V VRM. | Ensure that the 5-V VRM is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the 5-V VRM (see "Replacing the 5-V Power Supply VRM"). |
E0212 | VOLT 12 | System power supply is out of acceptable voltage range; faulty or improperly installed power supply. | Ensure that the power supplies are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the power supply (see "Power Supplies"). |
E0212 | VOLT BATT | Faulty battery or I/O riser card. | Replace the system battery (see "System Battery"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "Removing the I/O Riser Card"). |
E0212 | VOLT BP 12 | Backplane board is out of acceptable voltage range. | Ensure that the power supply fault indicator is not lit. If lit, replace the power supply (see "Power Supplies"). If the problem persists, ensure that the power cables are securely connected to the backplane board. If the problem persists, replace the SCSI backplane (see "Removing the SCSI Backplane"). |
E0212 | VOLT BP 3.3 | ||
E0212 | VOLT BP 5 | ||
E0212 | VOLT CPU VRM | Microprocessor VRM voltage is out of acceptable range; faulty or improperly installed microprocessor VRM; faulty microprocessor board. | Ensure that supported VRMs of the same type are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the VRM (see "VRMs"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E0212 | VOLT NIC 1.8V | Integrated NIC voltage is out of acceptable range; faulty or improperly installed I/O riser card; faulty or improperly installed power supply. | Ensure that the power supply fault indicator is not lit. If lit, replace the power supply (see "Power Supplies"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "Memory Riser Cards"). |
E0212 | VOLT NIC 2.5V | ||
E0212 | VOLT MEMORY n | Specified memory riser card is out of acceptable voltage range; faulty or improperly installed memory card; faulty or improperly installed power supply. | Ensure that the power supply fault indicator is not lit. If lit, replace the power supply (see "Power Supplies"). If the problem persists, ensure that the memory riser card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the memory riser card (see "Memory Riser Cards"). |
E0212 | VOLT PLANAR REG | Microprocessor board is out of acceptable voltage range; faulty or improperly installed microprocessor board. | Replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E0276 | CPU VRM n | Specified microprocessor VRM is faulty, unsupported, or improperly installed. | Ensure that supported VRMs of the same type are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the VRM (see "VRMs"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E0276 | MISMATCH VRM n | ||
E0280 | MISSING VRM n | Specified microprocessor VRM is improperly installed or missing. | Ensure that supported VRMs of the same type are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the VRM (see "VRMs"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E0319 | PCI OVER CURRENT | Faulty or improperly installed expansion card or I/O board. | Ensure that the expansion cards are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the expansion card(s) (see "Expansion Cards"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E0412 | RPM FAN n | Specified cooling fan is faulty, improperly installed, or missing | Ensure that the cooling are properly installed. if the problem persists, replace the faulty fans (see "Replacing a Cooling Fan"). |
E0780 | MISSING CPU 1 | Microprocessor is not installed in microprocessor socket 1. | Install a microprocessor in the specified socket (see "Microprocessors"). To identify microprocessor socket 1, see Figure 5-4. |
E07F0 | CPU IERR | Faulty or improperly installed microprocessor, microprocessor board, or I/O board. | Install a microprocessor (see "Microprocessors"). To identify microprocessor socket 1, see Figure 5-4. If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E07F1 | TEMP CPU n HOT | Specified microprocessor is out of acceptable temperature range and has halted operation. | Ensure that the system cooling fans are operating properly. If not, replace the faulty fan (see "Replacing a Cooling Fan"). If the problem persists, ensure that the specified microprocessor heat sink(s) are properly installed (see "Microprocessors"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor. |
E07F4 | POST CACHE | Faulty or improperly installed microprocessor or microprocessor board. | Replace the microprocessor (see "Microprocessors"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E07F4 | POST CPU REG | ||
E07F4 | POST CPU SMI | SMI handler failed to initialize; faulty or improperly installed I/O riser card, I/O board, or microprocessor board. | Replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card'). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E07FA | TEMP CPU n THERM | Specified microprocessor is out of acceptable temperature range and is operating at a reduced speed, or frequency. | Ensure that the system cooling fans are operating properly. If not, replace the faulty fan (see "System Fans"). If the problem persists, ensure that the specified microprocessor heat sink(s) are properly installed (see "Microprocessors"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor. |
E0876 | POWER PS n | No power is available from the specified power supply; specified power supply is improperly installed or faulty. | Ensure that the power cords are securely connected to the system. Ensure that the power supplies are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the faulty power supply (see "Power Supplies"). If the problem persists, replace the power distribution board (see "Power-Supply Distribution Board"). |
E0880 | INSUFFICIENT PS | Insufficient power is being supplied to the system; power supplies are improperly installed, faulty, or missing. | Ensure that the power supplies are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the faulty power supply (see "Power Supplies"). If the problem persists, replace the power distribution board (see "Power-Supply Distribution Board"). |
E0CB2 | MEM MIRROR | Uncorrectable memory error was remapped to the mirrored memory bank. | Informational only. |
E0CB2 | MEM SPARE BANK | Correctable errors threshold was met in a memory bank, and errors are remapped to the spare bank. | |
E0CF1 | MBE DIMM Bank n | Memory modules installed in the specified bank are not the same type and size; faulty memory module(s). | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
E0CF1 | POST MEM 64K | Parity failure in the first 64 KB of main memory. | Replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
E0CF1 | POST NO MEMORY | Main-memory refresh verification failure. | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
E0CF5 | LOG DISABLE SBE | Multiple single-bit errors on a single memory module. | Replace the memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
E0D76 | DRIVE FAIL | Faulty or improperly installed hard drive or RAID controller. | Ensure that the hard drives are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the faulty hard drive (see "Hard Drives"). If the problem persists, replace the RAID controller (see "Expansion Cards"). |
E0F04 | POST CMOS | CMOS write/read failure; faulty or improperly installed I/O riser card, I/O board, or microprocessor board. | Replace the I/O riser card (see "Removing the I/O Riser Card"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E0F04 | POST CPU SPEED | Microprocessor speed control sequence failure. | Replace the microprocessor (see "Microprocessors"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E0F04 | POST DMA INIT | DMA initialization failure; DMA page register write/read failure. | Ensure that the memory riser cards are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E0F04 | POST DMA REG | Faulty I/O board. | Replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E0F04 | POST KYB CNTRL | Faulty keyboard controller; faulty I/O riser card. | Ensure that the I/O riser card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
E0F04 | POST MEM RFSH | Main-memory refresh verification failure. | Ensure that the memory riser cards are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
E0F04 | POST PIC REG | Master or slave PIC register test failure. | Replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E0F04 | POST SHADOW | BIOS shadowing failure. | Ensure that the memory riser cards are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E0F04 | POST SHD TEST | Shutdown test failure. | |
E0F04 | POST SIO | Super I/O chip failure; faulty I/O riser card. | Ensure that the I/O riser card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "Removing the I/O Riser Card"). |
E0F04 | POST TIMER | Programmable interval timer test failure; faulty I/O board. | Replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E0F0B | POST ROM CHKSUM | Faulty or improperly installed expansion card. | Ensure that the expansion cards are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the expansion card (see "Expansion Cards"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E0F0C | VID MATCH CPU n | Specified microprocessor is faulty, unsupported, improperly installed, or missing. | Ensure that the microprocessor is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor (see "Microprocessors"). |
E10F3 | LOG DISABLE BIOS | BIOS disabled logging errors. | Check the SEL for details on the errors. |
E13F2 | IO CHANNEL CHECK | Faulty or improperly installed expansion card or I/O board. | Ensure that the expansion cards are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the expansion card (see "Expansion Cards"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E13F4 | PCI PARITY | ||
E13F5 | PCI SYSTEM | ||
E13F8 | CPU BUS INIT | Faulty or improperly installed microprocessor, microprocessor board, or I/O board. | Ensure that the microprocessor is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor (see "Microprocessors"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
E13F8 | CPU BUS PARITY | Faulty microprocessor board. | |
E13F8 | CPU MCKERR | Machine check error; faulty or improperly installed microprocessor or microprocessor board. | |
E13F8 | HOST BUS | Faulty or improperly installed I/O board or microprocessor board. | |
E13F8 | HOST TO PCI BUS | ||
E13F8 | MEM CONTROLLER | Faulty or improperly installed memory riser card or microprocessor board. | Ensure that the memory riser cards are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
E1580 | MISSING MEM n | Specified memory riser card is faulty or improperly installed. | Ensure that the memory riser cards are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the memory riser cards (see "Memory Riser Cards"). |
E1580 | POWER CONTROL | Faulty power-supply distribution board. | Replace the power-supply distribution board (see "Power-Supply Distribution Board"). |
E20F1 | OS HANG | Operating system watchdog timer timed out. | Restart your system. If the problem persists, see your operating system documentation. |
EFFF0 | ESM ERROR | ESM firmware failure; faulty I/O riser card. | Ensure that the I/O riser card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
EFFF1 | POST ERROR | BIOS error. | Update the BIOS firmware (see "Obtaining Technical Assistance"). |
EFFF2 | BP ERROR | Faulty or improperly installed backplane board; loose or improperly connected backplane board cables. | Ensure that the interface cables are securely connected to the backplane board. If the problem persists, replace the SCSI backplane (see "SCSI Backplane Board"). |
EFFF3 | DRAC ERROR | Faulty or improperly installed remote access card. | Ensure that the remote access card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the remote access card (see "Expansion Cards"). |
When a single message appears on the LCD, locate the code in Table 3-6 and perform the suggested corrective action. The code on the LCD can often specify a very precise fault condition that is easily remedied. For example, if the code E0280 MISSING VRM 2 appears, you know that a microprocessor is installed in socket 2, but the VRM for that microprocessor is either improperly installed or missing.
In contrast, you might be able to determine the problem if multiple related errors occur. For example, if you receive a series of messages indicating multiple voltage faults, you might deduce that the problem is a failing power supply.
For faults associated with sensors, such as temperature, voltage, fans, and so on, the LCD message is automatically removed when that sensor returns to a normal state. For example, if temperature for a component goes out of range, the LCD will display the fault; when the temperature returns to the acceptable range, the message is removed from the LCD display. For other faults, you must take some action to remove the message from the display:
Any of these actions will remove fault messages and return the status indicators and LCD colors to the normal state. Messages will reappear under the following conditions:
System messages appear on the console during POST to notify you of a possible problem with the system. If you are performing console redirection, system messages will appear on the console. Table 3-7 lists the system messages that can occur and the probable cause and corrective action for each message.
 |
NOTE: If you receive a system message that is not listed in Table 3-7, check the documentation for the application program that is running when the message appears or the operating system's documentation for an explanation of the message and recommended action. |
|
Message |
Causes |
Corrective Actions |
|---|---|---|
Address mark not found | Faulty diskette/CD drive subsystem or hard-drive subsystem; faulty peripheral riser card. | Ensure that the diskette/CD drive subsystem, hard drives, and peripheral riser card are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the faulty hard drive (see "Hard Drives"). If the problem persists, replace the peripheral riser card (see "Peripheral Riser Card"). |
Alert! Redundant memory disabled! Memory configuration does not support redundant memory Alert! Unsupported memory or incomplete sets in the following bank(s): Bank x | Memory modules installed are not the same type and size in all banks; faulty memory module(s). | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
Amount of available memory limited to 256 MB! | OS Install Mode is enabled in the System Setup program. | Disable OS Install Mode in the System Setup program (see "Using the System Setup Program"). |
Auxiliary device failure | Loose or improperly connected mouse or keyboard cable; faulty mouse or keyboard; faulty I/O riser card. | Check the mouse and keyboard connections. If the problem persists, replace the mouse and keyboard. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
BIOS Update Attempt Failed! | Remote BIOS update attempt failed. | Retry the BIOS update. If the problem persists, see "Obtaining Technical Assistance." |
Caution! NVRAM_CLR jumper is installed on system board. Please run SETUP | Incorrect configuration settings in System Setup program; NVRAM_CLR jumper is installed; faulty system battery. | Check the System Setup configuration settings (see "Using the System Setup Program"). Remove the NVRAM_CLR jumper (see Figure 5-2 for jumper location). |
CD-ROM drive not found | Improperly connected or missing CD drive. | Check the interface cable connection to the peripheral riser card. If the problem persists, replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the peripheral riser card (see "Peripheral Riser Card"). |
Checking embedded server management firmware | Embedded server management memory may be temporarily corrupted. | To clear the embedded server management memory, shut down the system, disconnect the power cords, wait approximately 30 seconds, reconnect the power cords, and then restart the system. |
CPU population error! | Faulty, improperly installed, or unsupported microprocessor. | Ensure that the microprocessors are properly installed and that they have the same level 2 cache size. If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor (see "Microprocessors"). |
CPU VRM Failure/missing/mismatch detected | Faulty, unsupported, or missing VRM(s). | Ensure that supported VRMs of the same type are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the VRM (see "Microprocessors"). |
CPUs with different level- 3 cache sizes detected | Microprocessors with different level 3 (L3) cache sizes are installed. | Ensure that all microprocessors have the same cache size and that they are properly installed (see "Microprocessors"). |
Data error | Faulty diskette, diskette drive, or hard drive. | Ensure that the diskette/CD drive subsystem, hard drives, and peripheral riser card are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the faulty hard drive (see "Hard Drives"). If the problem persists, replace the peripheral riser card (see "Peripheral Riser Card"). |
Decreasing available memory | Faulty or improperly installed memory modules. | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
Diskette drive n seek failure | Incorrect configuration settings in System Setup program. | Run the System Setup program to correct the settings (see "Using the System Setup Program"). |
Faulty or improperly installed diskette drive, or loose diskette/CD interface cable. | Ensure that the diskette/CD drive subsystem is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). | |
Diskette read failure | Faulty or improperly inserted diskette. | Replace the diskette. |
Diskette subsystem reset failed | Faulty diskette/CD drive controller; faulty peripheral riser card. | Ensure that the diskette/CD drive subsystem and peripheral riser card are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the peripheral riser card (see "Peripheral Riser Card"). |
Diskette write protected | Diskette write-protect feature enabled. | Move the write-protect tab on the diskette to disable the write-protect feature. |
Drive not ready | Faulty or improperly inserted diskette. | Insert the diskette properly in the diskette drive, or replace the diskette. |
Embedded server management error | Embedded server management memory may be temporarily corrupted. | To clear the embedded server management memory, shut down the system, disconnect the power cords, wait approximately 30 seconds, reconnect the power cords, and then restart the system. |
Embedded server management is not present | ||
Error: DRAC III initialization failure | Faulty remote access card or I/O board. | Ensure that the remote access card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the remote access card (see "Expansion Cards"). |
Error: DRAC III cannot be used with an add-in video card, system halted | The system supports only the embedded video when using a remote access card. | Remove the add-in video expansion card (see "Expansion Cards"). |
Error: DRAC III is not in the correct PCI slot, system halted | The remote access card is not in PCI slot 1. | Install the remote access card in PCI slot 1 (see "Expansion Cards"). |
Error: More than one DRAC III detected, system halted | The system supports only one remote access card. | Remove the remote access card(s) not in PCI slot 1 (see "Expansion Cards"). |
Extended Security Enabled! | Extended Security is enabled in the System Setup program. | |
Failed to copy memory Banks 1 & 2 to Banks 3 & 4 in Mirror mode | Faulty or improperly installed memory modules. | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
Gate A20 failure | Faulty keyboard controller; faulty I/O riser card. | Replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
General failure | Operating system corrupted or not installed properly. | Reinstall the operating system. |
I/O card parity interrupt at address | Faulty or improperly installed expansion card. | Ensure that the expansion cards are properly installed. If problem persists, replace the expansion card (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). |
IMB bus error | Faulty or improperly installed I/O board or microprocessor board. | Replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
Insufficient number of power supplies detected, system halted. | Insufficient power is being supplied to the system; specified power supply is improperly installed, faulty, or missing. | Ensure that the power supplies are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the power supply (see "Power Supplies"). |
Invalid configuration information - please run SETUP program | Incorrect configuration settings in System Setup program; NVRAM_CLR jumper is installed; faulty system battery. | Check the System Setup configuration settings (see "Using the System Setup Program"). Remove the NVRAM_CLR jumper (see Figure 5-2 for jumper location). If the problem persists, replace the system battery (see "System Battery"). |
Invalid ESCD Configuration, Resources Reallocated | System configuration data has been ignored. | Check the System Setup configuration settings (see "Using the System Setup Program"). |
Invalid SCSI Configuration; Daughter Card Detected, SCSI cable not present on connector A of the primary backplane. | SCSI cable is loose, improperly connected, or faulty. | Check the SCSI cable connection. If the problem persists, add or replace the SCSI cable (see "SCSI Backplane Board"). |
| ||
Invalid SCSI Configuration; Daughter Card Not Detected, SCSI cable present on connector B of the primary backplane. | SCSI channel B cable present; backplane daughter card is not installed. | Install the SCSI backplane daughter card (see "SCSI Backplane Board"). |
Invalid SCSI Configuration; SCSI cable not present on connector A of the primary backplane | SCSI cable is loose, improperly connected, or faulty. | Check the SCSI cable connection. If the problem persists, add or replace the SCSI cable (see "SCSI Backplane Board"). |
Keyboard controller failure | Faulty keyboard controller; faulty I/O riser card. | Ensure that the I/O riser card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
Keyboard data line failure | Loose or improperly connected keyboard cable; dirty or faulty keyboard; faulty keyboard controller; faulty I/O riser card. | Check the mouse and keyboard connections. If the problem persists, replace the mouse and keyboard. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
Keyboard failure | ||
Keyboard stuck key failure | ||
Memory address line failure at address, read value expecting value | Faulty or improperly installed memory modules; faulty microprocessor board. | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
Memory double word logic failure at address, read value expecting value | ||
Memory high address line failure at start address to end address | ||
Memory high data line failure at start address to end address | ||
Memory odd/even logic failure at start address to end address | ||
Memory write/read failure at address, read value expecting value | ||
Memory allocation error | Faulty application program. | Restart the application program. |
Memory bank population error! | Memory modules installed are not the same type and size in each bank; faulty memory module(s); memory modules are not installed in decreasing size with the largest size of memory modules in bank 1; memory modules are not installed sequentially. | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. Ensure that banks are populated sequentially (see "Memory Module Installation Guidelines"). If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
Memory parity failure at start address to end address | Faulty or improperly installed memory modules. | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). |
Memory parity error at address | ||
Memory parity interrupt at address | ||
Memory tests terminated by keystroke | POST memory test terminated by pressing the spacebar. | No action is required. |
No boot device available | Faulty or missing diskette/CD drive subsystem, hard drive, or hard-drive subsystem. | Check the Integrated Devices configuration settings in the System Setup program (see "Using the System Setup Program"). Ensure that either the SCSI Controller, Diskette Controller, or the IDE CD-ROM Controller is enabled. If the problem persists, replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the hard drive (see "Hard Drives"). If the system is booting from a RAID subsystem, reseat the RAID controller and check the SCSI cabling for an improper connection. |
No boot sector on hard- disk | No operating system on hard drive. | Check the hard-drive configuration settings in the System Setup program (see "Using the System Setup Program"). |
No microcode update loaded for Processor n | BIOS error. | Update the BIOS firmware. |
No timer tick interrupt | Faulty I/O board. | Replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
Non-system disk or disk error | Faulty diskette, diskette/CD drive assembly, hard drive, or hard-drive subsystem; no operating system on diskette or hard drive. | Use a bootable diskette. If the problem persists, replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the hard drive (see "Hard Drives"). |
Not a boot diskette | No operating system on diskette. | Use a bootable diskette. |
PCI BIOS failed to install | Loose cables to expansion card(s); faulty or improperly installed expansion card. | Ensure that all appropriate cables are securely connected to the expansion cards. If the problem persists, remove and reseat the expansion cards (see "Expansion Cards"). If the problem persists, replace the expansion card(s). |
PCI bus error | Faulty or improperly installed expansion card; faulty I/O board. | Remove and reseat the expansion cards (see "Expansion Cards"). If the problem persists, replace the expansion card(s). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
Plug & Play Configuration Error Embedded xxx | Error encountered in initializing PCI device; faulty I/O board. | Install the NVRAM_CLR jumper and reboot the system (see Figure 5-2 for jumper location). Remove and reseat the expansion cards (see "Expansion Cards"). If the problem persists, replace the expansion card(s). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). If the problem still persists, download and update the latest BIOS. |
Plug & Play Configuration Error PCI Slot n | Error encountered in initializing PCI adapter. | |
Primary backplane is not present | SCSI cable is loose, improperly connected, or faulty. | Check the SCSI cable connection. If the problem persists, add or replace the SCSI cable. |
Processor VID mismatching/VRM missing or failure detected | Faulty, unsupported, or missing VRM(s). | Ensure that supported VRMs of the same type are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the VRM (see "Microprocessors"). |
Read fault | Faulty diskette, diskette/CD drive assembly, hard drive, or hard-drive subsystem; faulty peripheral riser card. | Replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the hard drive (see "Hard Drives"). If the problem persists, replace the peripheral riser card (see "Peripheral Riser Card"). |
Requested sector not found | ||
Reset failed | Improperly connected drive interface or power cable. | Ensure that the interface cable is securely connected between the diskette/CD interposer board and the peripheral riser card. Ensure that the interface and power cables are securely connected to the backplane board (see Figure 5-5 for the backplane board). |
ROM bad checksum = address | Faulty or improperly installed expansion card. | Remove and reseat the expansion cards (see "Expansion Cards"). If the problem persists, replace the expansion card(s). |
Secondary backplane is not present | SCSI cable is loose, improperly connected, or faulty. | Check the SCSI cable connection. If the problem persists, add or replace the SCSI cable. |
Sector not found | Faulty diskette, diskette/CD drive assembly, or hard drive. | Replace the diskette. Replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the hard drive (see "Hard Drives"). |
Seek error | ||
Seek operation failed | ||
Shutdown failure | Shutdown test failure. | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. Ensure that banks are populated sequentially (see "Memory Module Installation Guidelines"). If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
System halted! Must power down | Wrong password entered too many times. | Informational only. |
Time-of-day clock stopped | Faulty battery or I/O riser card. | Replace the system battery (see "System Battery"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
Time-of-day not set - please run SETUP program | Incorrect Time or Date settings; faulty system battery. | Check the Time and Date settings (see "Using the System Setup Program"). If the problem persists, replace the system battery (see "System Battery"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
Timer chip counter 2 failed | Faulty I/O board. | Replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
Unable to access processor PROM | Faulty or improperly installed microprocessor; faulty microprocessor board. | Ensure that the microprocessors are properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor (see "Microprocessors"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
Unexpected interrupt in protected mode | Improperly installed memory modules or faulty keyboard/mouse controller; faulty I/O riser card. | Ensure that all banks contain memory modules of the same type and size and that they are properly installed. Ensure that banks are populated sequentially (see "Memory Module Installation Guidelines"). If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
Unsupported CPU combination | Microprocessor(s) is not supported by the system. | Install a supported microprocessor combination (see "Microprocessors"). If the problem still persists, download and update the latest BIOS. |
Unsupported CPU stepping detected | ||
Utility partition not available | <F10> key was pressed during POST, but no utility partition exists on the boot hard drive. | Create a utility partition on the boot hard drive (see "Using the Dell OpenManage Server Assistant CD" in your User's Guide). |
Verify that mouse and keyboard are securely attached to correct connectors. | Loose or improperly connected mouse or keyboard cable; faulty mouse or keyboard. | Check the mouse and keyboard connections. If the problem persists, replace the mouse and keyboard. |
Warning: Firmware is out- of-date, please update. | I/O riser card firmware error. | Update the I/O riser card firmware. |
Warning! SCSI cable not present on connector A or connector B of the primary backplane. | SCSI cables are loose, improperly connected, or faulty. | Check the SCSI cable connections. If problem persists, add or replace the SCSI cables. |
Warning: System FRU not programmed | Improperly installed I/O riser card, or corrupt or improperly programmed firmware. | Reseat the I/O riser card. If the problem persists, contact Dell. |
Write fault | Faulty diskette, diskette/CD drive assembly, hard drive, or hard-drive subsystem. | Replace the diskette. Replace the diskette/CD drive subsystem (see "CD and Diskette Drive"). If the problem persists, replace the hard drive (see "Hard Drives"). |
Write fault on selected drive |
When an error that cannot be reported on the monitor occurs during a boot routine, the system may emit a series of beeps that identify the problem.
When a beep code is emitted, record it on a copy of the Diagnostics Checklist in "Obtaining Technical Assistance," and then look it up in Table 3-8. If you are unable to resolve the problem by looking up the meaning of the beep code, use the system diagnostics to identify a more serious cause. If you are still unable to resolve the problem, see "Obtaining Technical Assistance."
 |
NOTE: If the system boots without a keyboard, mouse, or monitor attached, the system will not issue beep codes related to those peripherals. |
|
Code |
Cause |
Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|
1-1-2 | CPU register test failure | Replace microprocessor 1 (see "Microprocessors"). If the problem persists, replace microprocessor 2. |
1-1-3 | CMOS write/read failure; faulty or improperly installed I/O riser card, I/O board, or microprocessor board | Ensure that the I/O riser card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
1-1-4 | BIOS error | Reflash the BIOS firmware (see "Obtaining Technical Assistance"). |
1-2-1 | Programmable interval-timer failure; faulty I/O board | Replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
1-2-2 | DMA initialization failure | Remove and reseat the memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). If the problem persists, replace the specified memory modules. If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
1-2-3 | DMA page register write/read failure | |
1-3-1 | Main-memory refresh verification failure | |
1-3-2 | No memory installed | |
1-3-3 | Chip or data line failure in the first 64 KB of main memory | |
1-3-4 | Odd/even logic failure in the first 64 KB of main memory | |
1-4-1 | Address line failure in the first 64 KB of main memory | |
1-4-2 | Parity failure in the first 64 KB of main memory | |
1-4-3 | Fail-safe timer test failure | |
1-4-4 | Software NMI port test failure | |
2-1-1 through | Bit failure in the first 64 KB of main memory | |
3-1-1 | Slave DMA-register failure | Replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
3-1-2 | Master DMA-register failure | |
3-1-3 | Master interrupt-mask register failure | |
3-1-4 | Slave interrupt-mask register failure | |
3-2-2 | Interrupt vector loading failure | |
3-2-4 | Keyboard-controller test failure | Ensure that the I/O riser card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
3-3-1 | CMOS failure | Ensure that the I/O riser card is properly installed. If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
3-3-2 | System configuration check failure | |
3-3-3 | Keyboard controller not detected | |
3-3-4 | Video memory test failure | |
3-4-1 | Screen initialization failure | |
3-4-2 | Screen-retrace test failure | |
3-4-3 | Video ROM search failure | |
4-2-1 | No timer tick | |
4-2-2 | Shutdown test failure | |
4-2-3 | Gate A20 failure | |
4-2-4 | Unexpected interrupt in protected mode | Ensure that all the expansion cards are properly seated, and then reboot the system. |
4-3-1 | Improperly installed or faulty memory modules | Remove and reseat the memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). If the problem persists, replace the memory modules. If the problem persists, replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
4-3-2 | No memory modules installed in bank 1 | Install memory modules of the same type and size in bank 1 (see "Memory Modules"). |
4-3-3 | Faulty I/O board | Replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
4-3-4 | Time-of-day clock stopped | Replace the system battery (see "System Battery"). If the problem persists, replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
4-4-1 | Super I/O chip failure; faulty I/O riser card | Replace the I/O riser card (see "I/O Riser Card"). |
4-4-2 | BIOS-shadowing failure | Remove and reseat the memory modules (see "Memory Modules"). If the problem persists, replace the memory modules. If the problem persists, replace the I/O board (see "Expansion-Card Insulator and I/O Board"). |
4-4-3 | Microprocessor speed control sequence failure | Replace the microprocessor board (see "Microprocessor Board"). |
4-4-4 | Cache test failure; faulty microprocessor |
A warning message alerts you to a possible problem and asks you to take corrective action before the system continues a task. For example, before you format a diskette, a message may warn you that you may lose all data on the diskette. Warning messages usually interrupt the procedure and require you to respond by typing y (yes) or n (no).
 |
NOTE: Warning messages are generated by either the application program or the operating system. See your Installation and Troubleshooting Guide and the documentation that accompanied the operating system or application program. |
When you run a test group or subtest in system diagnostics, an error message may result. Diagnostic error messages are not covered in this section. Record the message on a copy of the Diagnostics Checklist (located in "Getting Help" in the Installation and Troubleshooting Guide), and then follow the instructions in that section for obtaining technical assistance.
The optional systems management software generates alert messages for your system. For example, the software generates messages that appear in the SNMP trap log file. Alert messages consist of information, status, warning, and failure messages for drive, temperature, fan, and power conditions. For more information, see the systems management software documentation.